SQL Connector
The SQL Connector allows you to connect to the following databases and perform multiple database actions:
• PostgreSQL
• SQL Server
• MySQL
• Oracle
Prerequisites for using Oracle database
Windows
1. On the machine where the ThingWorx Flow server is installed, follow this link to install the Oracle 11.2 client libraries.
2. Add these libraries to the system PATH.
3. Use the echo %PATH% command in a new Command Prompt window to verify that the path is updated.
4. Run the pm2 restart all --update-env command.
5. Refresh the ThingWorx Flow browser page.
|
|
Whenever your machine restarts, run the pm2 restart all --update-env command.
|
Linux
1. On the machine where the ThingWorx Flow server is installed, follow this link to install the Oracle 11.2 client libraries to enable connection to the Oracle database.
2. Create the flow.sh file under the /etc/profile.d directory.
3. In the flow.sh file, add the path to the Oracle library.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/oracle
4. Use the echo $LD_LIBRARY_PATH command in a new Command Prompt window to verify that the path is updated.
5. Run the pm2 restart all --update-env command.
6. Refresh the ThingWorx Flow browser page.
Connector Release Version
SQL Connector is delivered in the 8.5 release.
Supported Actions
• Get Rows
Supported Triggers
None
Supported Authorization
Basic
Add SQL Connector Connection
You need to authorize SQL Connector for each SQL Connector action. To authorize the SQL Connector, do the following:
1. Drag any action under SQL Connector to the canvas, place the pointer on the action, and then click  or double-click the action.
or double-click the action.
2. In the Database list, select the appropriate database.
3. In the selected database list, select Add New.
The Add Connection window opens.
For example, if you have selected PostgreSQL as the database, then in the PostgreSQL list, select Add New.
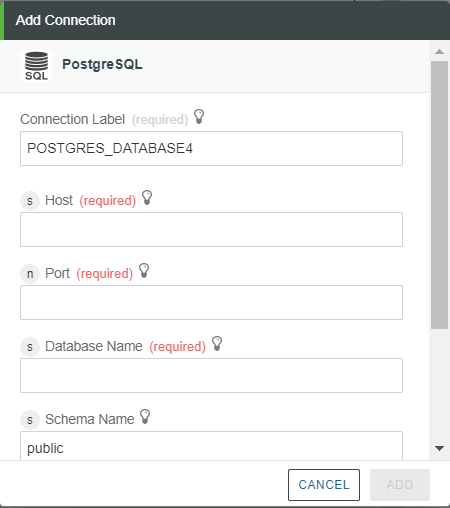
4. Edit the Connection Label field, if you want.
Do not use spaces, special characters, and leading numbers.
5. In the Host field, enter the database host.
6. In the Port field, enter the database port.
7. In the Database Name field, enter the name of the database.
For Oracle, the value of the Database Name field is the service name of the database. |
8. In the Schema Name field, enter the schema name. By default, this is set to the following:
◦ PostgreSQL — public
◦ SQL Server — dbo
◦ Oracle — user name
If you want to connect to the database of another user, then enter the user name of that user.
The MySQL database does not have a schema name. |
9. In the User Name and Password fields, enter the correct user name and password to authorize the database connection.
10. Click ADD to add the database connection.
A new connection is added to the list.
11. Click TEST to validate the database connection.
Customize the SQL Connector
The following table provides the list of data types and their supported operators:
Data Type | Supported Operators |
|---|---|
• INT • BIGINT • MEDIUMINT • SMALLINT • TINYINT • NUMBER • FLOAT • REAL • DECIMAL • NUMERIC • DOUBLE • DOUBLE PRECISION • SMALLSERIAL • SERIAL • BIGSERIAL • INTEGER • PRECISION • DEC • MONEY • SMALLMONEY | • GREATER THAN • GREATER THAN OR EQUAL TO • LESS THAN • LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO • EQUAL TO • NOT EQUAL TO • BETWEEN • NOT BETWEEN • IN • NOT IN • IS NULL • IS NOT NULL |
• TEXT • TINYTEXT • MEDIUMTEXT • LONGTEXT • NTEXT • CHAR • VARCHAR • VARCHAR2 • NCHAR • NVARCHAR • VARYING • CHARACTER • CHARACTER VARYING | • EQUAL TO • NOT EQUAL TO • LIKE • NOT LIKE • STARTS WITH • ENDS WITH • SUBSTRING • IS NULL • IS NOT NULL |
• DATE • DATETIME • DATETIME2 • TIME • TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE • TIMESTAMP • DATETIMEOFFSET • SMALLDATETIME • YEAR • INTERVAL | • BEFORE • AFTER • BETWEEN • NOT BETWEEN • IN • NOT IN • IS NULL • IS NOT NULL |
Any other data types | • EQUAL TO • NOT EQUAL TO • IS NULL • IS NOT NULL |
You can add an operator for any data type for the following actions:
• Delete Rows
• Get Rows
• Get Rows with Join
• Update Rows
To customize an operator, perform the following steps:
1. Create the data.json file as shown below:
{
"DatatypeOperatorConfig": [{
"dataTypeName":"Any_Data_Type",
"supportedDBs":["Database1","Database2"],
"Operators":[{
"id":"OPERATOR_ID",
"value":"OPERATOR"
}]
}]
}
"DatatypeOperatorConfig": [{
"dataTypeName":"Any_Data_Type",
"supportedDBs":["Database1","Database2"],
"Operators":[{
"id":"OPERATOR_ID",
"value":"OPERATOR"
}]
}]
}
For example, if you want to add the LIKE operator for Oracle database for unsupported data type, RAW, your data.json file must look like the following:
{
"DatatypeOperatorConfig": [{
"dataTypeName":"RAW",
"supportedDBs":["oracle"],
"Operators":[{
"id":"LIKE",
"value":"LIKE"
}]
}]
}
"DatatypeOperatorConfig": [{
"dataTypeName":"RAW",
"supportedDBs":["oracle"],
"Operators":[{
"id":"LIKE",
"value":"LIKE"
}]
}]
}
2. Browse to the path where you have saved the data.json file, and start Command Prompt.
3. Depending on your use case, run one of the following commands:
Scenario | Command |
|---|---|
Customize a specific database host name and port | flow-deploy settings file upload -f <Path to data.json file> -t <ThingWorx Flow URL> -u <ThingWorx Administrator User> -p <ThingWorx Administrator User Password> -c database - s <Database Host><Database Port> For example: flow-deploy settings file upload -f data.json -t <ThingWorx Flow URL> -u <ThingWorx Administrator User> -p <ThingWorx Administrator User Password> -c database -s localhost32776 |
Customize all connected instances of the database | flow-deploy settings file upload -f <Path to data.json file> -t <ThingWorx Flow URL> -u <ThingWorx Administrator User> -p <ThingWorx Administrator User Password> -c database -d |
4. Refresh the browser.
Now, when you drag one of the supported actions to the Workflow Editor, you should see the operator in the Operators list.