To Move and Rotate a Geometry
1. Perform one of the following actions depending on the mode:
◦ In part mode, select one or more surfaces or faces on a part geometry.
You can select the following items to move:
▪ Surfaces—One or more surfaces.
You can select any number of surfaces in the following combinations:
▪ Solid surfaces
▪ Solid surfaces and whole quilts
▪ Quilt surfaces selected from the same quilt
▪ Quilt surfaces selected from the same quilt, and other whole quilts
You cannot select the following combinations:
▪ Solid surfaces and individual surfaces selected from a quilt
▪ Quilt surfaces selected from different quilts
▪ Curves—One or more curves.
▪ Datums—One or more datums. The default datums at the top of the Model Tree are always copied, and the copy moves to a new location. The selection can include:
▪ Datums only, including different types of datums in the same selection.
▪ Datums and curves.
▪ Datums and surfaces.
◦ In assembly mode select multiple surfaces, quilts from multiple parts in combination with multiple components from one or more levels of the assembly geometry.
Hold down the CTRL key to select multiple surfaces.
The dragger appears on the selected surface. A Live Toolbar appears with
 Move and Rotate
Move and Rotate selected by default.
2. Click the arrow next to
 Move and Rotate
Move and Rotate and select a type for the movement:
◦ Choose Solution — Calculates a geometric solution automatically based on the movement type and the geometries selected.
◦ Create Side Surfaces — Performs a linear pull operation by creating side walls at the edge of the selection.
◦ Extend Side Surfaces — Extends the side walls to intersect with the moving geometry.
|  The selections shown in the collector in References. |
3. To define a new origin and orientation for the dragger, select a new reference in the graphics window. You can select a plane, surface, axis, coordinate system, or an edge as a reference. The dragger moves to the new location.
Click

to lock the
Place dragger collector. The
Place dragger collector remains active even after you reposition the dragger. This allows you to quickly change the dragger placement from one location to another location without reactivating the
Place dragger collector.
Alternatively, double-click
on the Options Toolbar to lock the
Place dragger collector.
|  Locking the Place dragger collector is recommended if you want to move or rotate the geometry with multiple dragger placement references. |
Click

to unlock the
Place dragger collector. To reposition the dragger, click the
Place dragger collector and then select a reference in the graphics window.
Alternatively, double-click
on the Options Toolbar to unlock the
Place dragger collector.
|  You can reposition the dragger to another geometry in the graphics window (or Model Tree) and drag the handles to move the selected geometry. While moving the geometry, you can snap the cursor to a reference by holding down the SHIFT key and pointing to the desired reference. See Example: Moving a Surface with the Dragger on an Axis. |
4. To move the selected geometry, pull the dragger. A displacement value appears in the Offset value box. Or type a displacement value in the Offset value box.
5. To rotate the selected geometry, pull the angular dragger. A value appears in the Angle value box. Or type a value in the Angle value box.
6. To select curves and datum references to be moved with surfaces selected in step 1, click the
Curves and datums collector. Select from the model tree or the Graphics Window. Alternatively, if the Floating Dashboard is collapsed, click
on the Options Toolbar.
7. Select the
Maintain tangency check box to keep existing tangency between the modified surface and directly adjacent surfaces of the geometry. If Floating Dashboard is collapsed, click

.
| • Use default conditions check box is available if Maintain tangency check box is selected. It is used to set system defined conditions for the selected and surrounding geometry. • Click the arrow below Use default conditions check box to see conditions. |
8. Do the following to assign system defined conditions:
a. Click the Condition collector (below Use default conditions check box) to activate it.
b. Select one or more surfaces, edges or vertices from the graphics window.
c. Select one of the following conditions:
▪ Fixed: Fix a surface, edge or vertex
▪ Fixed with tangency: Fix a surface while maintaining tangency to neighbouring dragged surfaces or surface regions
▪ Fixed axis: Fix an axis or a surface of revolution
▪ Fixed center: Fix the centre point of a sphere or a torus
▪ Fixed normal: Fix the normal direction of a planar surface
▪ Constant R1 : Keep the radius of revolution of a torus constant
▪ Constant R2: Keep the radius of the section of a torus constant
▪ Constant angle: Keep the cone angle constant
▪ Fixed pole: Fix the apex of a cone
▪ Propagate through: Allow changes to a round surface and the neighbouring tangent surface to keep tangency
▪ Fix underlying edge: Fix a point on the underlying edge which has been rounded or chamfered
▪ Constant R: Keep the radius of a cylinder or sphere constant
▪ Keep spherical: Prevent a sphere from becoming a torus
9. Click Add to create a condition between the selected geometries.
Click Remove to remove a selected condition from the list of conditions.
Click Remove All to remove all the conditions from the list of conditions.
10. Select the Keep original geometry check box to keep a copy of the original geometry in addition to moving it. Available when Attach geometry check box is selected.
11. To snap a geometry to a reference, click the Snapping reference collector and select surface to snap. Hold down the SHIFT key, move the dragger and select a reference.
12. Depending on your selection in step 2, perform the following actions:
◦ If you have selected Choose Solution or Extend Side Surfaces in step 2, the following appears:
▪ To reattach the modified geometry to the same solid or quilt surface where it was originally attached, selected in step 1, keep the
Attach geometry check box selected. If Floating Dashboard is collapsed, click

.
▪ To store the attachment properties when you reattach the modified geometry to the model, select the Store attachment properties check box. Available when Attach geometry check box is not selected. Attachment properties specify how a selected modified geometry reconnects to the rest of the model.
▪ To recreate the rounds or chamfers if they were a part of the original geometry and the modified geometry is attached to the surface, keep the Recreate rounds and chamfers check box selected. Available when Attach geometry check box is selected.
◦ If you have selected
Choose Solution in step 2, the
Solutions area appears. Click the

or

one or more times to calculate new geometric solutions. Alternatively, select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list.
|  After computing several solutions if you move the geometry by dragging a handle, change the dragger reference, or modify the dimensions for the move operation, all the computed solutions are removed from the list. The new default solution is added to the list. |
13. To select a bounding edge reference:
a. Select the Attach geometry check box.
b. Click the Bounding edges collector.
c. Select one or more edges from the Graphics Window.
14. To preview one or more geometric solutions, click

or

one or more times. Or select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list.
15. Click Maintain rounds and chamfers check box to keep round and chamfer attributes (radius and type) connecting the selected geometry to the rest of the model.
If Maintain rounds and chamfers check box is not selected, then round or chamfer is treated as part of the selected geometry.
16. Middle-click to complete.
 Move and Rotate selected by default.
Move and Rotate selected by default. Move and Rotate selected by default.
Move and Rotate selected by default. Move and Rotate selected by default.
Move and Rotate selected by default. Move and Rotate and select a type for the movement:
Move and Rotate and select a type for the movement: to lock the Place dragger collector. The Place dragger collector remains active even after you reposition the dragger. This allows you to quickly change the dragger placement from one location to another location without reactivating the Place dragger collector.
to lock the Place dragger collector. The Place dragger collector remains active even after you reposition the dragger. This allows you to quickly change the dragger placement from one location to another location without reactivating the Place dragger collector. on the Options Toolbar to lock the Place dragger collector.
on the Options Toolbar to lock the Place dragger collector. to unlock the Place dragger collector. To reposition the dragger, click the Place dragger collector and then select a reference in the graphics window.
to unlock the Place dragger collector. To reposition the dragger, click the Place dragger collector and then select a reference in the graphics window. on the Options Toolbar to unlock the Place dragger collector.
on the Options Toolbar to unlock the Place dragger collector.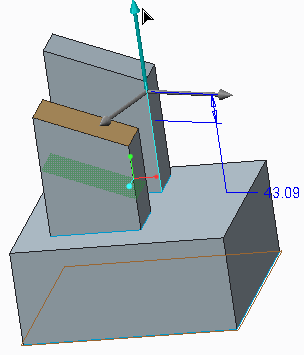
 on the Options Toolbar.
on the Options Toolbar. .
. .
. or
or  one or more times to calculate new geometric solutions. Alternatively, select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list.
one or more times to calculate new geometric solutions. Alternatively, select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list. or
or  one or more times. Or select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list.
one or more times. Or select a pre calculated value from the adjacent list.