Service Flow Manager Process Flow
SFM Transaction Designer also known as SFM is the central engine in ServiceMax that helps you define the flow of information across various service delivery processes. SFM allows you to maintain the accuracy and consistency of such information throughout the service delivery cycle. It also helps reduce the time spent in each step.
The following flow diagram demonstrates a typical use case and flow of SFM.
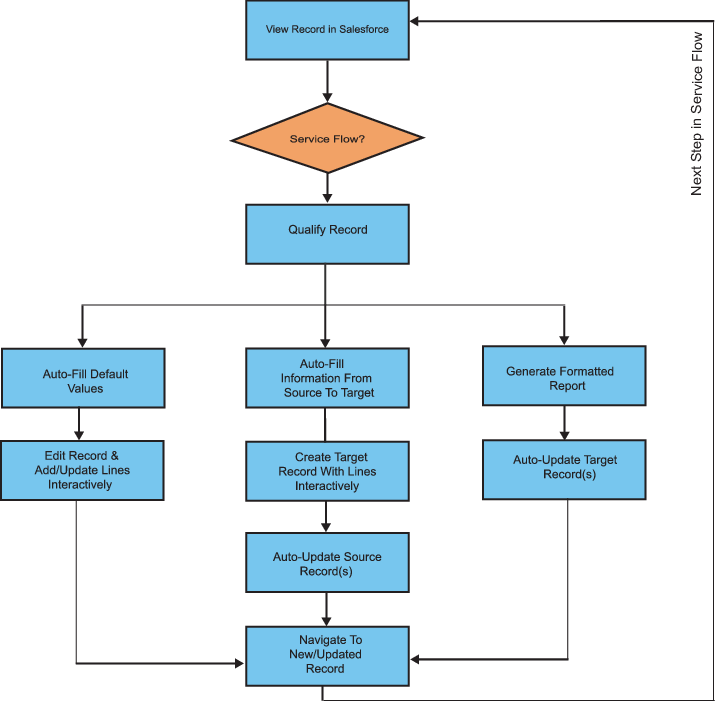
Components of Service Flow Manager
• SFM Transaction Manager: Comprises the SFM Transaction, Docs Designer, and the SFM Delivery Engine. It helps define various service flows based on business requirements. Supporting SFM configurations include expressions, maps, data validation rules, formulas, page layouts, and smart document templates.
• SFM Wizard: Comprises the SFM Wizard Designer and the SFM Wizard Delivery. This enables the grouping of related service flows as steps in a wizard. The wizard and the steps facilitate the guided execution of service flow based on the business context.
• SFM Search: Comprises the SFM Search Designer and SFM Search Delivery. This facilitates the definition of multi-object searches in one screen, with options to configure search fields, search result fields, sort order, and pre-filters.
• Data Lookup Rules: Comprises the Data Lookup Rules configuration and the delivery using Data Lookup Rules Engine. This provides a powerful, generic, and configurable mechanism to match fields of any two objects and apply a configurable field map from matched object to the target object.
This configuration group includes the following options to configure all the service flows applicable to online and mobile apps:
• SFM Transaction and Docs Designer, used to manage the configuration of SFM transactions for various field service flows and Smart Docs for generation of reports.
• SFM Custom Actions, used to configure service flow actions of type web service and URL.
• SFM Wizards, used to define wizards for sequential launching of SFM transactions and other SFM processes, based on business process flow.
• Inventory Processes, used to configure processes related to inventory management, which includes managing Product Stock, Stocked Serial, and Stock History records.
• SFM Search, used to manage search configurations for one or more objects, with predefined filters, search fields, and search results page layouts.
• SFM Expressions, Mappings, and Data Validation Rules, used to manage the configuration of expressions (qualifying criteria), mappings from field to field/value, and rules to validate data entered in SFM transactions.
• Scheduled SFM, used for scheduled execution of certain types of SFM transactions and services in the background, without user interaction.
• Data Lookup Rules, used for matrix-type matching and mapping of data from any object to any object.