Configuring Work Order Duration for PM Work Orders
In the Time-Based PM Plan templates, you can configure the Work Order Duration for the PM work orders associated with the PM plan. This enables you to define the exact duration required for technicians to complete the task and minimizes delays. To configure Work Order Duration, see Creating Time-Based PM Plan templates.
|
|
The Work Order Duration field is not available for Condition-Based PM Plan templates.
|
Use Case
Iniscope company wants to schedule a one-year of monthly preventive maintenance visits for a solar panel system installation to avoid future breakdowns or critical maintenance issues. Also, you want to configure the exact work order duration required to complete the work order to 30 days.
You can configure the Time-Based PM Plan Template with the Work Order Duration as shown in the following screenshot:
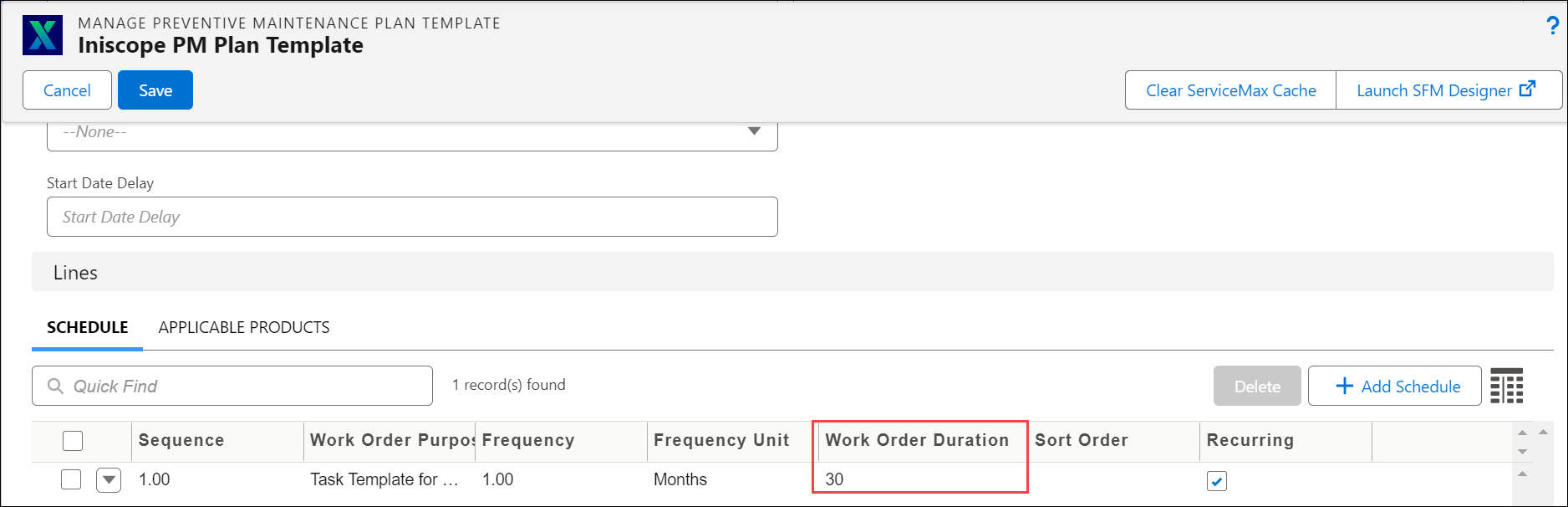
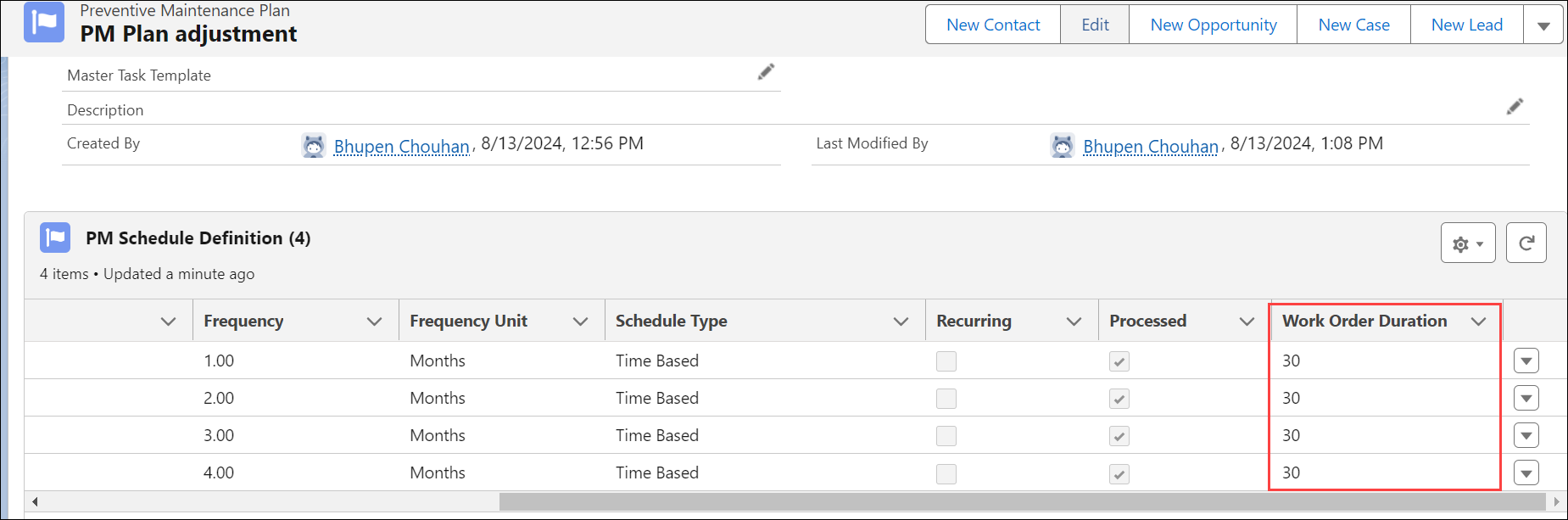
Based on the configured work order duration, the PM Scheduler runs at the specified frequency and creates work orders for the qualified PM Plan. The Work Order Duration from the PM Plan Template is mapped to the PM Scheduled Definition of the PM Plan.
In the work order records, the Preferred End Time is populated by combining the Preferred Start Time with the Work Order Duration.
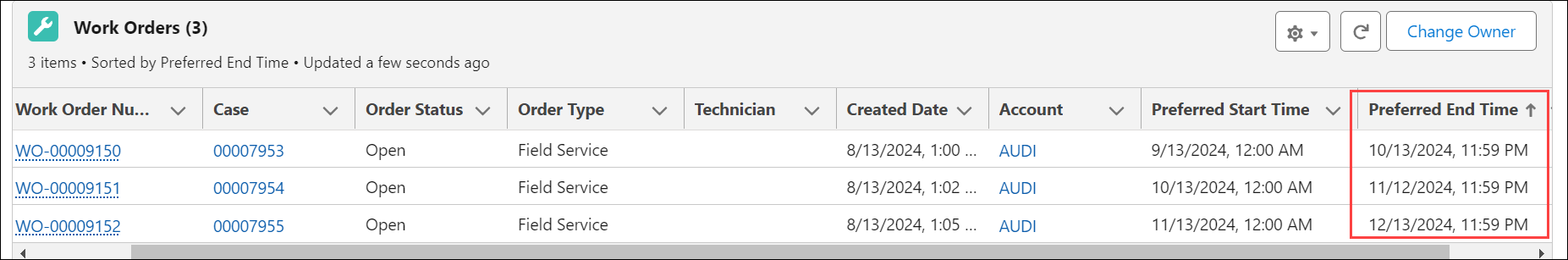
If the work order duration is not configured in the PM Plan template, then the Preferred End Time is calculated based on the frequency of the PM Schedule. |
When you create a PM Template by selecting the "Generate all Recurrences Upon Creation" checkbox, configuring the Work Order Duration ensures that the PM Plan generates work orders with consistent intervals. This prevents the Preferred End Date from extending beyond the original recurring frequency.
The Work Order Duration field is updated in the following SFMs: • Create Preventive Maintenance Plan Template • Manage Preventive Maintenance Plan Template • Manage Account based Preventive Maintenance Plan • Manage Location based Preventive Maintenance Plan • Manage Product based Preventive Maintenance Plan |