To Convert a Solid Part into a Sheet Metal Part
1. Open a part with a solid body.
2. Follow one of the steps below.
◦ Click > > . The active solid body is selected by default, you can select a different solid body.
◦ Select a solid body in the Model Tree, right-click and select  Convert to Sheet Metal.
Convert to Sheet Metal.
 Convert to Sheet Metal.
Convert to Sheet Metal.The Convert tab opens.
3. If the solid body has geometry:
◦ For thin protrusions, use the  Driving Surface tool.
Driving Surface tool.
 Driving Surface tool.
Driving Surface tool.◦ For block-like geometry, use the  Shell tool.
Shell tool.
 Shell tool.
Shell tool.4. If the solid body has no geometry, use the  Empty Body tool.
Empty Body tool.
 Empty Body tool.
Empty Body tool.Using the Driving Surface Tool
Starting with Creo Parametric 5.0, when you convert a solid body to a sheet metal body you select a driving surface and the system finds an offset surface to obtain a constant wall thickness. The system then considers adjacent surfaces with the same thickness to include automatically in the conversion. Additional surfaces you select to include will have the same wall thickness. You can select surfaces to exclude as well. Use the options to recreate rounds and chamfers.
1. Click  Driving Surface.
Driving Surface.
 Driving Surface.
Driving Surface.2. The References tab opens by default.
a. Select the body to convert.
b. Select a surface to use as the driving surface for the sheet metal body. The selected surface shows in the Driving surface collector. Adjacent surfaces that meet the thickness criteria are selected as well.
c. To include surfaces that are treated as face surfaces in the sheet metal body, click the Include surfaces collector and select one or more surfaces.
d. To exclude surfaces so that they are not treated as face surfaces in the sheet metal body, click the Exclude surfaces collector and select one or more surfaces.
3. Click Options to set one of the following options:
◦ Adjacent Rounds & Chamfers treatment—Controls the inclusion of rounds and chamfers in the sheet metal part.
▪ Recreate—Removes rounds and chamfers and recreates them after the part is converted to a sheet metal part.
▪ Remove—Removes the rounded geometry. The resulting geometry is similar to the geometry before the round operation.
▪ Ignore—Ignores the rounded geometry. The resulting geometry is without the rounded geometry.
The following rounds and chamfers are supported for these options: • Rounds—Round design objects and automatically detected rounds even when there is no existing design object. • Chamfers—Chamfer design objects. |
◦ Keeps not classified surfaces as a separate quilt—Keeps surfaces that are not classified as the driving surface, additional surfaces, and excluded surfaces as separate quilts.
◦ Set driving surface opposite selected surface—Sets the surface opposite the selected driving surface as the driving surface.
4. In the Thickness box, set a value for the wall thickness.
5. Click 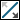 to flip the direction of thickness.
to flip the direction of thickness.
 to flip the direction of thickness.
to flip the direction of thickness.6. Click  . The Convert tab closes, the body is converted to a sheet metal body, and the part is converted to a sheet metal part. The Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the body is converted to a sheet metal body, and the part is converted to a sheet metal part. The Sheetmetal tab opens.
 . The Convert tab closes, the body is converted to a sheet metal body, and the part is converted to a sheet metal part. The Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the body is converted to a sheet metal body, and the part is converted to a sheet metal part. The Sheetmetal tab opens.7. Create additional features as needed.
Using the Shell Tool
1. Click  Shell.
Shell.
 Shell.
Shell.2. In the Thickness box, set a value for the wall thickness.
3. Click  to flip the direction of thickness.
to flip the direction of thickness.
 to flip the direction of thickness.
to flip the direction of thickness.4. The References tab opens by default.
a. Select the body to convert.
b. Select one or more surfaces to remove from the part.
5. Click  . The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
 . The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.6. Create additional features as needed.
Using the Empty Body Tool
An empty body is a body that has no geometry.
1. Click  Empty Body.
Empty Body.
 Empty Body.
Empty Body.2. The References tab opens by default.
a. Select the body to convert.
3. Click  . The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
 . The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.
. The Convert tab closes, the part is converted to a sheet metal part, and the Sheetmetal tab opens.4. Create additional features as needed.