Example: Sheet Metal Convert Operation
These examples depict both methods of using the Convert tool. Use the Shell method for block-like parts. Use the Driving Surface method for thin protrusions with constant thickness.
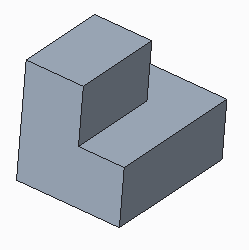
The following figures show converting a solid part to a sheet metal part using the shell conversion method and removing a surface
• The original part
• The orange surfaces are selected, the green mesh surfaces are surfaces selected to remove.
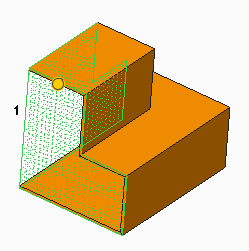
1. Surfaces selected to remove
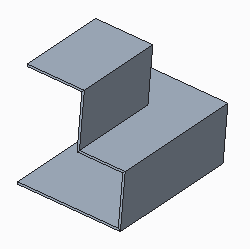
• The resulting part
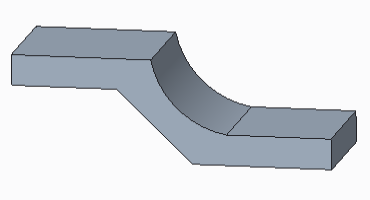
The following figures show converting a solid part without uniform thickness to a sheet metal part.
• The original solid part
• Selecting the driving surface.
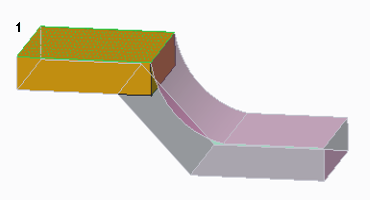
1. Driving surface
• Selecting an additional surface, note that the adjacent surface is automatically selected.
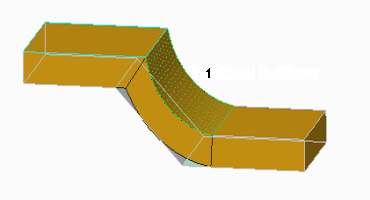
1. Selected additional surface
• Resulting sheet metal part.
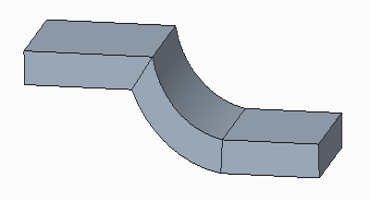
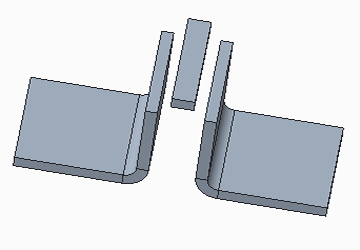
The following figures show converting a solid part with disjoint volumes to a sheet metal part.
• The original part.
• Selecting the driving surface.
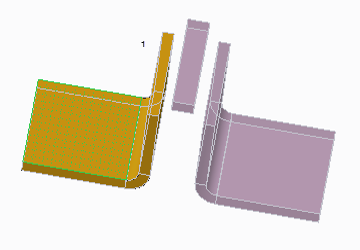
1. Driving surface
• Selecting additional surfaces.
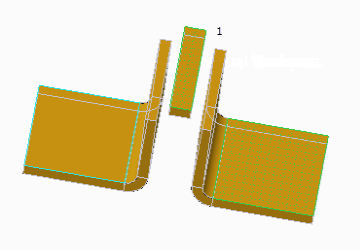
1. Additional surfaces selected
• The resulting sheet metal part

The following figures show converting a solid part with forms and non-uniform thickness.
• The original part.
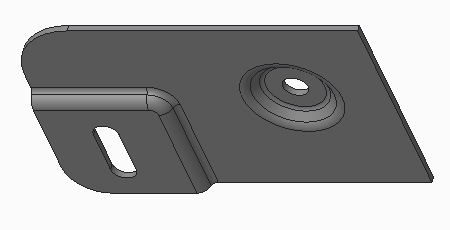
• Selecting the driving surface.
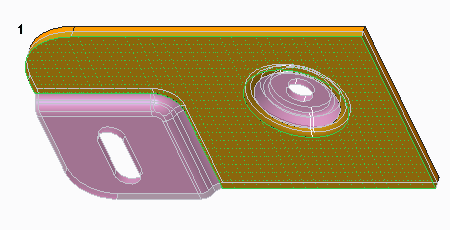
1. Driving surface
• Selecting additional surfaces
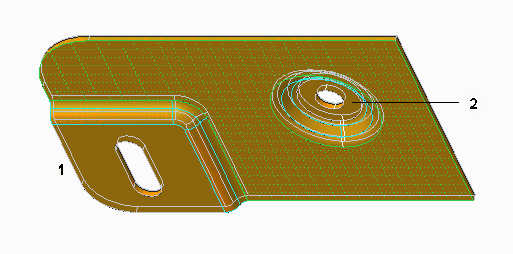
1. Driving surface
2. Additional surface