Preventive Maintenance Workflow
The Preventive Maintenance Workflow includes the following stages:
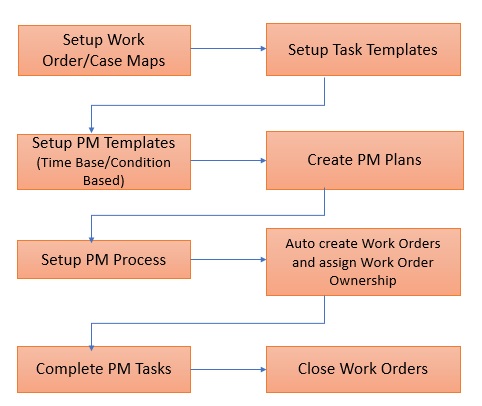
1. Define field mappings: Admin defines the field mappings for the following:
◦ PM Schedule Definition to Work Order
◦ Installed Product/Account to Work Order (as needed)
◦ Location to Work Order (as needed)
◦ Task Template to Task
◦ Required Part to Work Details
2. Create Task Template (Optional): Admin creates a Task Template with tasks and parts details. Creating Tasks or Required Parts within the Task Template is also optional. For example, an admin can create a Task Template with only Required Parts and no Tasks, or vice-a-versa.
3. Create PM Plan Template: Admin creates a PM Plan Template (Time-Based or Condition-Based) with PM Schedule Templates and applicable products. The user can associate Task Templates (known as Work Order Purpose) to the PM Schedule Templates on the PM Plan Template. The PM Plan Template can then utilize the task template reference when generating a PM Plan with PM Schedule Definitions to create Tasks and/or Parts Required on the generated PM Work Order.
4. Configure PM Process: Admin configures a PM Process which picks up the qualified PM Plans and creates Work Orders according to the rules specified in the PM Process.
5. Create PM Plan: End-user creates a PM Plan from the Account, Installed Product, Location, or Service Contract by utilizing the appropriate PM Plan Template. The PM Plan is created with PM coverages, PM schedules, and PM Schedule Definition.
The PM Scheduler runs at regular intervals based on the frequency. For plans that are due as per the schedule, PM Scheduler creates Work Orders and Cases as defined in the PM Plan and assigns them to technicians, dispatchers, or queues as configured in the PM Plan. The technician can then close out the tasks. Statistical information is automatically posted to the PM Plan when the Work Order is closed.
Examples
After the PM is configured for your organization, you define the field mapping required to create PM Work Orders or Cases automatically. The type of field mappings defined depends on your organization’s requirements. Some of the examples are:
• If your organization requires one PM Work Order for all products covered in a PM Plan, you must configure a field mapping between Service Contract and Work Order fields.
• If your organization needs one PM Work Order for each installed product, you must create mapping between Installed Product and Work Order fields.
• If you prefer to create PM Cases for PM Work Orders, appropriate field mappings must also be defined for Cases as well. Field mappings include standard ServiceMax fields and any custom fields created from your organization. You must not create and execute PM Plans without any field maps.