Object Mappings
To simplify the business process, the Object Mappings feature allows you to easily map data between two objects so that mapping can be used in a flow.
Object Mappings include field mappings between source and target object records, and value mappings for target object records. It helps the end-user to get the field data pre-populated with respect to the connected objects.
Object Mapping Types
There are the following types of mapping between the objects:
• Field Mapping: In this type of mapping, both the source and target must be present. The target object field is mapped with the compatible source object field. Field, Function, and Value are the three available options for field mapping. When the target object field is mapped with the source object field, at least one mapping is compulsory. For example, when a Case is created from an Asset record, this mapping allows the values in the fields such as Account and Asset to map to the Case's Account and Asset fields. For example, you can map a Standard object field to a Custom object field. Select a Standard object as Source and a Custom object as the target. Alternatively, you can select a Custom object as the source and a Standard object as the target. In the following screen, Custom Object Application Log is selected as the source object and Standard Object Account is selected as the target object:
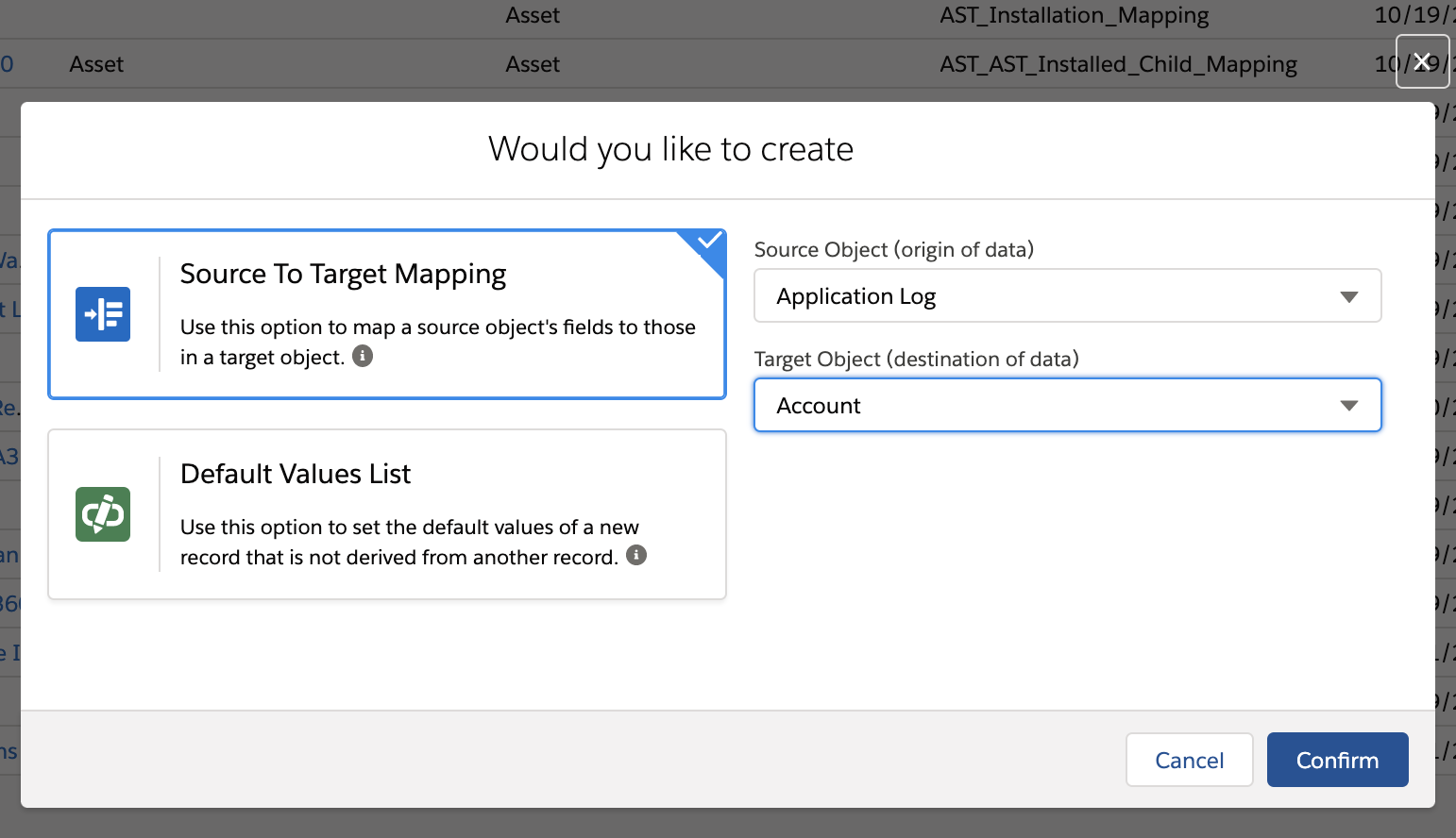
• Value Mapping: This type of mapping is used to set default values when a new child record is created. For value mapping, only Value and Function options are available. For example, when a technician adds a new Product Consumed record on a work order, the Quantity Consumed default value is set to 1.
The Function option is available only for the Date and DateTime fields of the objects. |