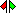

 on the Semaphore's icon indicates that the item is a stub.
on the Semaphore's icon indicates that the item is a stub.The Class box on the Options tab of a Semaphore's Property Pages shows the Class, Data Type or Interface that owns the Operations that implement the Semaphore. |
 Dependency - The Dependency is owned jointly by the Semaphore and the other associated item. The access permissions you have to a Dependency are determined by the access permissions of the dependent item.
Dependency - The Dependency is owned jointly by the Semaphore and the other associated item. The access permissions you have to a Dependency are determined by the access permissions of the dependent item. Class - The linked Class contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Class to Semaphore symbol on diagram).
Class - The linked Class contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Class to Semaphore symbol on diagram). Data Type - The linked Data Type contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Data Type to Semaphore symbol on diagram).
Data Type - The linked Data Type contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Data Type to Semaphore symbol on diagram). Interface - The linked Interface contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Interface to Semaphore symbol on diagram).
Interface - The linked Interface contains the Operations required to implement the Semaphore (drag Interface to Semaphore symbol on diagram).Like most other items in a Model, a Semaphore can be linked to an
Activity Partition,
Comment,
Frame Box,
General Node,
General Flow,
General Flow Diagram Node,
Constraint (applied),
General Flow Diagram Flow or
Swimlane. |