|
Type of Weld
|
Example
|
Key Dimensions
|
|
Fillet (T joint)
|
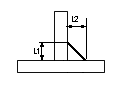 |
L1 - First leg distance
L2 - Second leg distance
|
|
Fillet (corner joint)
|
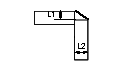 |
L1 - First leg distance
L2 - Second leg distance
|
 , light fillet welds are represented by
, light fillet welds are represented by  , and surface fillet welds are represented by
, and surface fillet welds are represented by  .
.