To Create a Clearance Hole
1. Click > . The Hole tab opens.
2. Click  Standard to create a standard hole. The standard hole options are shown.
Standard to create a standard hole. The standard hole options are shown.
 Standard to create a standard hole. The standard hole options are shown.
Standard to create a standard hole. The standard hole options are shown.3. Under Profile, click 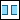 Clearance to create a clearance hole.
Clearance to create a clearance hole.
 Clearance to create a clearance hole.
Clearance to create a clearance hole.4. Select a surface on the model on which to place the hole. The selection is highlighted and the default placement Type is set to 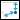 Linear. This is your placement reference.
Linear. This is your placement reference.
 Linear. This is your placement reference.
Linear. This is your placement reference.• You can select the placement reference before you select the hole tool. • The default placement type varies according to the selection of the placement reference. For a surface reference, the default type is  Linear. Linear.• You can change the hole placement type by selecting the new type from the Type box on the Placement tab. |
5. Drag the offset placement reference handles to the appropriate references to constrain the hole. As you drag each handle, the available references are highlighted as your pointer moves over them. The system automatically snaps the handle to the reference and adds them to the Offset References collector on the Placement tab.
6. To orient the hole to be parallel to or perpendicular to a reference:
a. Click the Placement tab, click the Hole orientation collector, and select a planar, axial, or linear reference.
b. Click 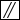 to make the hole parallel to the orientation reference, or click
to make the hole parallel to the orientation reference, or click 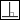 to make the hole perpendicular to the orientation reference.
to make the hole perpendicular to the orientation reference.
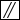 to make the hole parallel to the orientation reference, or click
to make the hole parallel to the orientation reference, or click 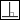 to make the hole perpendicular to the orientation reference.
to make the hole perpendicular to the orientation reference.7. In the  Thread type list, select the industry-standard hole chart (ISO, UNC, or UNF).
Thread type list, select the industry-standard hole chart (ISO, UNC, or UNF).
 Thread type list, select the industry-standard hole chart (ISO, UNC, or UNF).
Thread type list, select the industry-standard hole chart (ISO, UNC, or UNF).8. In the  Screw size box, type or select a screw size.
Screw size box, type or select a screw size.
 Screw size box, type or select a screw size.
Screw size box, type or select a screw size.If you enter a screw size that is not available in the list, the system selects the closest screw size. You can also drag the hole diameter handle to select a screw size. |
9. Select the required drill depth type from the drill depth type list. By default, the drill depth is set to  To Next, drill up to the next surface.
To Next, drill up to the next surface.
 To Next, drill up to the next surface.
To Next, drill up to the next surface.10. To add countersink to the hole:
a. Click 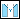 Countersink on the Hole tab.
Countersink on the Hole tab.
 Countersink on the Hole tab.
Countersink on the Hole tab.b. To define the countersink diameter or angle, click the Shape tab, and type or select a new countersink 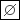 diameter or countersink angle in the corresponding boxes.
diameter or countersink angle in the corresponding boxes.
 diameter or countersink angle in the corresponding boxes.
diameter or countersink angle in the corresponding boxes.11. To add counterbore to the hole:
a. Click  Counterbore on the Hole tab.
Counterbore on the Hole tab.
 Counterbore on the Hole tab.
Counterbore on the Hole tab.b. To define the counterbore diameter or depth, click the Shape tab and type or select a new counterbore  diameter or counterbore depth in the corresponding boxes.
diameter or counterbore depth in the corresponding boxes.
 diameter or counterbore depth in the corresponding boxes.
diameter or counterbore depth in the corresponding boxes.12. To represent the hole with lightweight geometry, click  Lightweight.
Lightweight.
 Lightweight.
Lightweight.13. To ensure that the entire top of the hole intersects the outside of the solid geometry, on the Shape tab, make sure that the Top Clearance check box is selected.
You can define the default state of the Top Clearance check box by setting the default_hole_top_clearance configuration option.
14. To set the fit of the clearance hole, on the Shape tab, select an option:
◦ Close Fit—Creates a fit intended for the accurate location of parts which must assemble without perceptible play.
◦ Medium Fit—Creates a fit suitable for ordinary steel parts or for shrink fits on light sections. The medium fit is the tightest fit that can be used with high-grade cast iron external members.
◦ Free fit—Creates a fit intended for use where accuracy is not essential, where large temperature variations are likely to be encountered, or both.
You can define the default fit by setting the default_fit_clearance_hole configuration option.
15. To select the bodies from which geometry is removed, click the Body Options tab and select an option:
◦ To cut geometry from all the bodies that the feature passes through, select All.
◦ To cut geometry from selected bodies:
1. Select Selected.
2. Click the body collector, and then select bodies from which to cut geometry.
16. Click  OK.
OK.
 OK.
OK. Hole
Hole