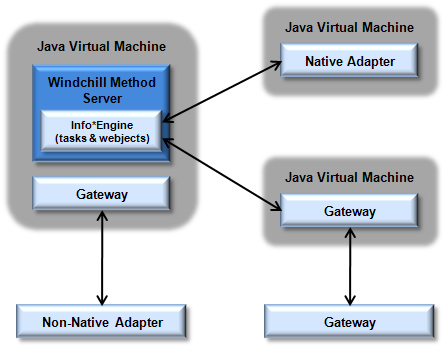
Using Out-of-Process Adapters and Gateways
Distributing adapters across multiple hardware systems reduces the overall resource usage on the machine hosting the Info*Engine code; however, it does introduce some delay and resource usage associated with using a TCP/IP connection for communicating between Info*Engine components and each adapter.
The following diagram shows the communication lines that are used when three adapters and one gateway are distributed.
Distributed native adapters and gateways are installed and run in their own Java Virtual Machine (JVM). These virtual machines can be on the same hardware system as the Info*Engine server or on a different hardware system. Non-native adapters can only be configured as out-of-process adapters, and they always run as separate processes. Although gateways for non-native adapters are typically configured as in-process gateways to minimize the communication delays, they do not need to be in the same process.
The deployment of distributed adapters at your site may be determined by a company policy that requires the adapter to be located near the application it accesses, or it may be based on administrative reasons. One reason for running a native adapter in its own Java Virtual Machine could be to better manage the resource usage of the virtual machine.