Package mapping for C++ (C++ code)
For each Package, ACS generates a subfolder or namespace. In addition, if a Package owns any Attributes, Operations or Type Definitions, ACS generates a header file and implementation file for the Package, which is derived from properties of the Package, the items it owns, and the tagged values set for the Tag Definitions that are applied by the «C++ Namespace» and «C++ Package » stereotypes.
• If the Package owns Attributes, the Attributes are generated in the header and implementation files created for the Package. For Attribute mapping information, see Attribute mapping for C++ (C++ code). Example code
• If the Package owns Basic Types, the Basic Types are ignored.
• If the Package owns Classes, header and sometimes implementation files are generated for each Class. For Class mapping information, see Class mapping for C++ (C++ code).
• If the Package owns Data Types, header and sometimes implementation files are generated for each Data Type. For Data Type mapping information, see Data type mapping for C++ (C++ code).
• If the Package owns Dependencies, ACS typically generates #includes in the code. For Dependency mapping information, see Dependency mapping for C++ (C++ code). Example code
• If the Package owns Interfaces, a header file is generated for each Interface. For Interface mapping information, see Interface mapping for C++ (C++ code).
• If the Package owns Operations, the Operations are generated in the header and implementation files created for the Package. For Operation mapping information, see Operation mapping for C++ (C++ code). Example code
• If the Package owns Packages, each Package is generated as a folder or namespace.
ACS is not designed to generate Folder Packages that are children of a Namespace Package. |
• If the Package owns Signals, header and sometimes implementation files are generated for each Signal. For Signal mapping information, see Signal mapping for C++ (C++ code).
• If the Package owns Type Definitions, the Type Definitions are generated in the header and implementation files created for the Package. For Type Definition mapping information, see Definition mapping for C++ (C++ code). Example code
• If the Mapping property of a Package is set to Folder, ACS generates the Package as a subfolder of the root directory. In the following example, the Package1 and Package2 Packages both have Folder mapping and are generated as subfolders of the root directory. 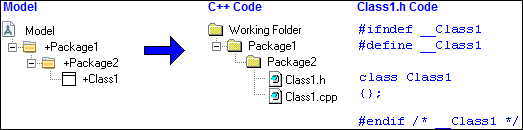

• If the Mapping property of a Package is set to Namespace, ACS generates the Package as a namespace. In the following example, the Namespace1 Package is generated as a namespace in the Class1 header file.
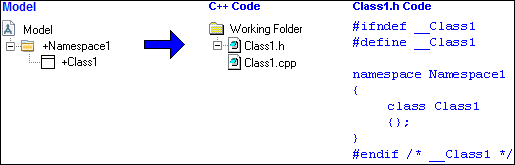
• The Name property is generated as the name of the header and implementation files.
ACS may modify the package name that is added to the code to make it valid for C++. You can specify the exact package name to add to the code through the CODE_GENERATION_NAME property of a Package. Tell me more... |
• The Visibility property of a Package is ignored.
The following tag definitions are applied to a Package by the «C++ Namespace» stereotype:
• If the tagged value of the C++ Anonymous Item tag definition is set to TRUE, it means that the namespace is used as an anonymous type and is generated with no name. Example code
Reverser Notes: When reverse engineering a namespace that is used as an anonymous type, the Reverser creates a Package in Modeler and sets its C++ Anonymous Item tag definition to TRUE. The name of the Package is as follows:unnamed<integer to make unique>
• If the tagged value of the C++ Using Decls tag definition has been set, the value is generated as the using declarations for the namespace.
If the C++ Using Decls and C++ Using Directives tag definitions are both blank, ACS will generate a 'using namespace std' statement when necessary.
• If the tagged value of the C++ Using Directives tag definition has been set, the value is generated as the using directives for the namespace.
If the C++ Using Directives and C++ Using Decls tag definitions are both blank, ACS will generate a 'using namespace std' statement when necessary.
The following tag definitions are applied to a Package by the «C++ Package» stereotype:
• If the tagged value of the C++ Header Include tag definition has been set, the value is generated at the beginning of the header file so that you can generate your own #includes to files that are not modeled in the Model. Note that you can use Dependencies to generate #includes to other Packages, Classes, Data Types, Interfaces and Signals that are modeled in the Model.
• If the tagged value of the C++ Implementation Include tag definition has been set, the value is generated at the beginning of the implementation file so that you can generate your own #includes to files that are not modeled in the Model. Note that you can use Dependencies to generate #includes to other Packages, Classes, Data Types, Interfaces and Signals that are modeled in the Model.