Example: Region Growing
The reg_grow function divides an image into several homogenous connected regions using a region-growing algorithm. Region-based segmentation is used to group regions in an image that bear homogeneous properties, such as intensity, texture, and so on.
For information on using this example, refer to About Image Processing Examples.
1. Create an image with several rectangular boxes:
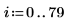
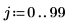
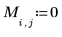
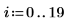 | 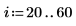 | 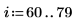 |
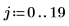 | 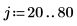 | 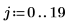 |
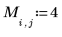 | 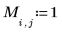 | 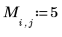 |
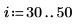 | 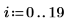 | 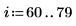 |
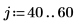 | 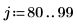 | 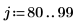 |
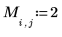 | 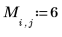 | 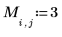 |
2. Use the runif function to add zero-mean uniform-distributed noise within [-0.1 0.1]:
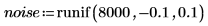
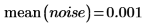
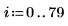
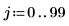
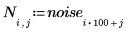
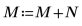
3. Use the scale function to scale the image, and then use the WRITEBMP function to save the image to a file. View the image.
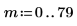
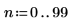
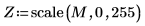
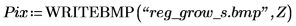

(reg_grow_s.bmp)
4. Use the region-growing algorithm:
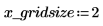
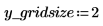
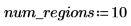
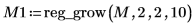
5. View the output in false color to make the regions more obvious.
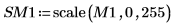
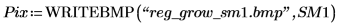

(reg_grow_sm1.bmp)
6. Use the gray_to_rgb function to convert the gray image to color. View the output in false color to make the regions more obvious.

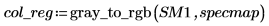
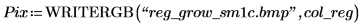

(reg_grow_sm1c.bmp)
7. Verify the number of regions found by the algorithm and then use the imhist function to take a look at the histogram.
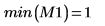
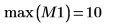
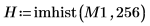
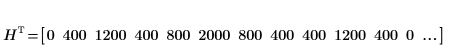
As in the input matrix, there are five regions with area of 400, two regions of 800, and three regions of 2000.
8. Apply this segmentation to a real image, an MRI image of a person's head.
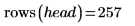
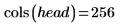
9. Use the submatrix function to extract the first 256 rows from the image to avoid having an odd number of rows.
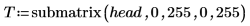
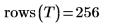
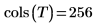
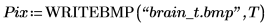
10. Apply the region growing procedure to this image starting with an initial 2 x 2 partition and ending with 20 regions:
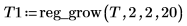
11. Display the original image next to the segmented and scaled image.
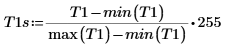
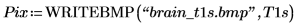
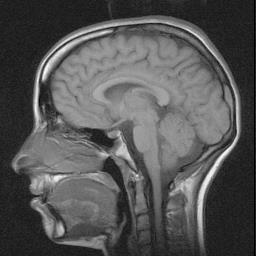 |  |
(brain_t.bmp) | (brain_t1s.bmp) |
12. Select all points in the segmented image which have the same value as the selected spoint.
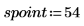
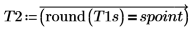
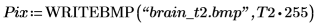
T2 is a binary image:

(brain_t2.bmp)
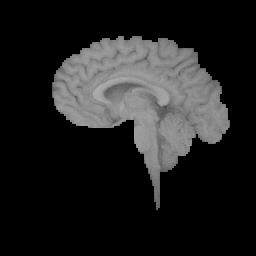
(brain_extract.bmp)