Example: Median and Quantile Filtering
Use medsmooth and getnoise to find the median intensity (0.5 quantile) of each element in an image and its eight nearest neighbors (3 x 3 square kernel). The medsmooth function returns the filtered image while getnoise returns the difference between the original and filtered image.
Use quantfilt if user-defined kernel and quantile are required instead of the median.
In addition to removing noise, median filtering also tends to remove sharp, small features from a picture.
For information on using this example, refer to About Image Processing Examples.
medsmooth
1. Read in an image.
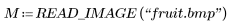
2. Add noise to the image.
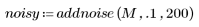
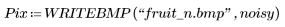
3. Compare the original and the noisy image.
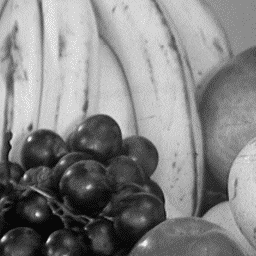 (fruit.bmp) | 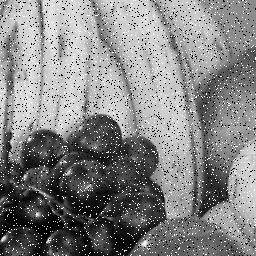 (fruit_n.bmp) |
4. Filter the image with medsmooth.

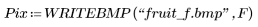
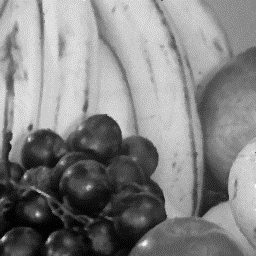
(fruit_f.bmp)
getnoise
This function subtracts the original version of an image matrix from its median filtered version.
1. Apply the getnoise function to the noisy image.

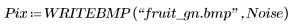
(fruit_gn.bmp)
The getnoise function performs the equivalent of subtracting the noise from the filtered image:
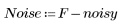
2. Calculate and view the absolute difference between the two images.
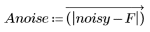
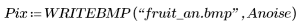

(fruit_an.bmp)
quantfilt
In some cases, the median filter with square 3 x 3 kernel may not be general enough to do the correct filtering. For instance, if an image with many sharp corners is filtered in this way, corner pixels are often removed. Avoid this effect by using the quantfilt function with a plus-shaped median-filtering kernel rather than the uniform 3 x 3 kernel specified above.
Consider the usual pattern and add some noise to it:
1. Read in the pattern image.
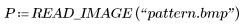
2. Add noise to the image.
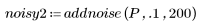
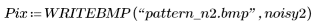
3. Compare the original and the noisy image.
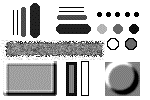 (pattern.bmp) |  (pattern_n2.bmp) |
4. Filter the noisy image using the quantfilt function with a 0.5 quantile for the median value and a 3 x 3 square kernel.
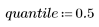
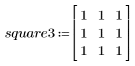

5. Filter the noisy image using the quantfilt function with a 0.5 quantile for the median value and a cross-shaped kernel.
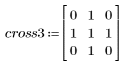
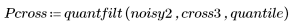
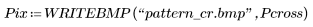
6. Compare the two filtered patterns.
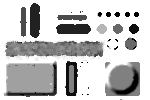 (pattern_sq.bmp) |  (pattern_cr.bmp) |
The square kernel degrades the square edges, lines, and corners much more than the cross-shaped kernel.
Nonmedian Quantiles
Another application of the quantfilt function is to choose quantiles other than the median (0.5) value, which changes the overall intensity of the image. For instance, if we choose the 0.0 quantile, we take the minimum value of the pixel and its neighbors; the 1.0 quantile gives the maximum value. (These are somewhat similar to gray-scale morphological erosion and dilation)
1. Cause darker regions of the original pattern to dilate and lighter regions to erode by setting quantile to 0.0.
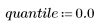
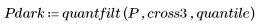
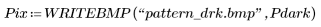
2. Cause lighter regions of the original pattern to dilate and darker regions to erode by setting quantile to 1.0.
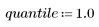
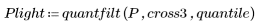
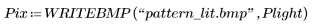
3. Compare the original pattern with the dark and light versions.
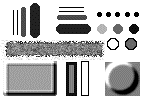 (pattern.bmp) |  (pattern_drk.bmp) | 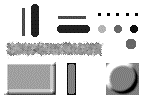 (pattern_lit.bmp) |