To Move and Copy Style Curves
1. Click > > or > > .
2. Click the  collector and select one or more curves. You can also select a circle or an arc.
collector and select one or more curves. You can also select a circle or an arc.
 collector and select one or more curves. You can also select a circle or an arc.
collector and select one or more curves. You can also select a circle or an arc.3. To remove any references to the original geometry that is being copied, select the Unlink check box. To retain all references to the original geometry that is being copied, clear the Unlink check box.
4. You can translate, scale, or rotate the geometry while you copy or move it.
◦ Translate operation
Use any of these methods to translate curves:
▪ Drag the curves in the graphics window.
In the Move box, select an option to specify the direction constraint while translating the geometry:
▪ Free—Geometry moves freely.
▪ Normal—Geometry moves along the normal of the active datum plane. Alternatively, hold down the ALT key while you drag the geometry.
▪ H/V—Geometry moves parallel to the active datum plane either along the horizontal direction only or along the vertical direction only. Alternatively, hold down the CTRL and ALT keys simultaneously while you drag the geometry.
▪ Specify move coordinate values.
Click the Options tab, and under Move, type x-, y-, and z-coordinate values. To treat the x-, y-, and z-coordinate values as offsets from the geometry's original position, select the Relative check box.
◦ Scale operation
Use any of these methods to scale curves:
▪ Drag the handles on the marquee.
▪ In the Scale box, select an option to specify the scale type:
▪ Center—Scales uniformly around the center of the marquee. Alternatively, hold down the SHIFT and ALT keys simultaneously while you drag the marquee.
▪ Opposite—Scales uniformly in the opposite direction of the selected corner, edge, or face.
▪ Drag the handles:
▪ Drag any corner of the marquee for three-dimensional scaling.
▪ Drag the edge handle for two-dimensional scaling.
▪ Drag an edge arrow for one-dimensional scaling.
▪ Specify scale coordinate values:
Click the Options tab, and under Scale, type x-, y-, and z-coordinate values. To lock scale values for the x-, y-, and z-coordinates, click  . To unlock the values, click
. To unlock the values, click 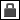 .
.
 . To unlock the values, click
. To unlock the values, click  .
.◦ Rotate Operation
Use the rotation jack to rotate the geometry.
▪ Orient the jack
The rotation axes are defined by the orientation of the jack. In the Transform box, select an option to specify the transform type:
▪ Selection—Transforms the selected curves with the marquee. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Transform Selection from the shortcut menu.
▪ Marquee—Transforms only the marquee and the rotation jack. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Transform Marquee from the shortcut menu.
▪ Set the rotation center
The rotation center is defined by the location of the jack.
▪ To change the rotation center, click anywhere on the jack away from the end handles, and drag the jack to a new location.
▪ To place the jack in the center of the marquee, click the Jack tab and under Rotation, click 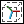 . Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Center Jack from the shortcut menu.
. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Center Jack from the shortcut menu.
 . Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Center Jack from the shortcut menu.
. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Center Jack from the shortcut menu.▪ To align the jack with the active plane, click the Jack tab and under Rotation, click 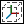 . Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Align Jack from the shortcut menu.
. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Align Jack from the shortcut menu.
 . Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Align Jack from the shortcut menu.
. Alternatively, right-click the rotation jack and choose Align Jack from the shortcut menu.▪ Rotate the geometry
Use any of these methods to rotate curves:
▪ Drag the handles on the ends of the jack to rotate the geometry.
▪ Specify rotate coordinate values.
Click the Options tab, and under Rotate, type x-, y-, and z-coordinate values.
5. Click  .
.
 .
. Style
Style Copy
Copy Move
Move