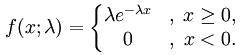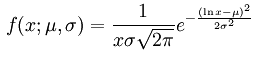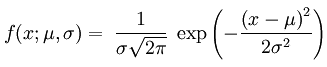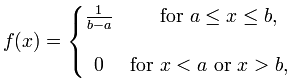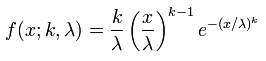About a Statistical Design Study
A Statistical Design Study allows you to assign statistical distributions to dimensions and parameters that are design variables and to parameters that are design goals of a Multi-Objective Design Study (MODS). Using the response surface corresponding to a MODS (MODSRS) and the statistical distributions assigned to the corresponding design variables, Creo Parametric runs a large number of approximate experiments to determine the distribution parameters of the design goals of a MODS. You can use the results of a statistical design study to find a “close to optimal” operating point for your design goals.
The following table lists the available types of statistical distributions, the equations that they use, and the parameters they generate:
|
Statistical Distribution
|
Equation
|
Parameters
|
|
Exponential
|
|
λ: rate
|
|
Lognormal
|
|
μ: mean
σ: standard deviation
|
|
Normal
|
|
μ: mean
σ: standard deviation
|
|
Uniform
|
|
No parameters
|
|
Weibull
|
|
λ: scale
k: shape
|
You can select a type of statistical distribution for the design goals of a MODS. Accordingly, the distribution parameters that provide the best fit to the sampling of the response surface are computed. The Normal type of statistical distribution is selected by default for the design variables listed under the Design Variables section and for the design goals listed under the Design Goals section in the Statistical Design Study dialog box.
Methods of conducting a statistical design study are as follows:
• Single—A single operating point is used for the study and all the samples are in the neighborhood of the operating point according to the statistical distributions of the design variables. In case of Lognormal and Normal types of statistical distributions, the operating point is the mean of the distribution.
• MODS—Points uniformly distributed in the design space of MODSRS are used for the study. The design goals for the statistical design study are the statistical distribution parameters of the goals of the original MODS. The number of operating points is equal to the number of experiments specified for the MODS. For each operating point, a statistical design study is conducted and the statistical distribution parameters for the design goals are computed. These parameters are displayed under the Table Data section in the Multi-Objective Design Study dialog box. The column names for these parameters appear in the format DISTRIBUTIONPARAMETERNAME-DESIGNGOALNAME. For example, Standard Deviation for an analysis feature having the name LENGTH:CIRCUMFERENCE_1 is displayed in the format STANDARD_DEVIATION-LENGTH:CIRCUMFERENCE_1.
You can apply limits such as Lower Limit and Upper Limit to the design goals. Based on the applied limits, Creo Parametric calculates the Defects Per Million Units (DPMU) and the standard deviations that the limits are away from the mean value. These standard deviations are represented as upper and lower n x Sigma. In the system generated graph in the Design Goal Statistical Properties dialog box, vertical red lines indicate the values of the user-defined limits and shaded red areas indicate the regions of defects, that is the number of experiments that fall outside the user-defined limits.
|
|
 In six-sigma projects, design goals are defined such that the limits for rejecting them are six standard deviations away, on either side of the mean value. This indicates that 99.9997% of the goals are within these limits. Plus or Minus 3 sigma indicates that 93.3% of the goals are acceptable. |
You can save a study to disk using the Save command and open it later when you return to the model. Saving a study saves the design variables along with their statistical distribution types and parameters. However, the design goals are saved only with the statistical distribution type assigned to them. The distribution parameters for the design goals must be computed again.