|
Functions
|
Supported in Native or FEM mode
|
Definitions
|
|
sin(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
standard trigonometric function.
|
|
cos(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
standard trigonometric function.
|
|
tan(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
standard trigonometric function.
|
|
sinh(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
hyperbolic trigonometric function.
|
|
cosh(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
hyperbolic trigonometric function.
|
|
tanh(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
hyperbolic trigonometric function.
|
|
asin(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
arc sine in range – 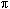 /2 to /2 to  /2. /2. |
|
acos(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
arc cosine in range 0 to  . . |
|
atan(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
arc tangent in range –  /2 to /2 to  /2. /2. |
|
atan2(y,x)
|
Native, FEM
|
arc tangent of y/x in range –  to to  . . |
|
exp(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
exponential function ex.
|
|
ln(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
natural (base e) logarithm.
|
|
log(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
base 10 logarithm.
|
|
abs(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
absolute value. If x>=0 returns x, otherwise –x.
|
|
sqrt(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
square root.
|
|
min(x,y)
|
Native, FEM
|
returns the minimum of x and y. If x<y returns x, otherwise y.
|
|
max(x,y)
|
Native, FEM
|
returns the maximum of x and y. If x>y, returns x, otherwise y.
|
|
sign(x,y)
|
Native, FEM
|
sign transfer of y to x. If y<0 returns–abs(x), otherwise abs(x).
|
|
mod(x,y)
|
Native, FEM
|
remainder function, that is x–int(x/y)*y where int() means "integer part of". The sign of the result is always the same as the sign of x.
|
|
if(c,x,y)
|
Native, FEM
|
"if" test, or switching function. If expression c (the "condition") returns non-zero (true) then the if function returns x, otherwise (if c=0.0) it returns y. Read like this: if c then x else y.
|
|
bound(x,lo,hi)
|
Native, FEM
|
limits x to be between bounds lo and hi. If x<lo returns lo, if x>hi returns hi, otherwise, returns x. lo must be <=hi.
|
|
dead(x,lo,hi)
|
Native, FEM
|
provides a "dead zone" when x is between lo and hi. If x<lo returns x–lo, if x>hi, returns x–hi, otherwise returns 0.
|
|
ceil(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
"ceiling" function, rounds toward positive infinity
|
|
floor(x)
|
Native, FEM
|
rounds toward negative infinity
|
|
near(x,y,delta)
|
Native, FEM
|
"nearness" test. Returns 1.0 (true) if x is within delta of y. If abs(x–y)<=delta returns 1.0, otherwise returns 0.0.
|
|
pow(x,y)
|
FEM
|
exponentiation function x y. The base is x and exponent is y.
|
|
Constants:
|
||
|
pi
|
Native, FEM
|
 = 3.14159... = 3.14159... |
|
e
|
Native
|
 = 2.71828... = 2.71828... |
|
Arithmetic Operators:
|
||
|
+
|
Native, FEM
|
add
|
|
–
|
Native, FEM
|
subtract, unary minus, negate
|
|
*
|
Native, FEM
|
multiply
|
|
/
|
Native, FEM
|
divide
|
|
^
|
Native, FEM
|
exponentiate
|
|
Logical Operators (these operators return 1.0 for true, 0.0 for false):
|
||
|
!
|
Native, FEM
|
unary "not"
|
|
==
|
Native, FEM
|
equal
|
|
!=
|
Native, FEM
|
not equal
|
|
<
|
Native, FEM
|
less than
|
|
>
|
Native, FEM
|
greater than
|
|
<=
|
Native, FEM
|
less than or equal to
|
|
>=
|
Native, FEM
|
greater than or equal to
|
|
&& in Native mode
& in FEM mode
|
Native, FEM
|
logical AND
|
|
|| in Native mode
| in FEM mode
|
Native, FEM
|
logical OR
|
|
Grouping Operators:
|
||
|
( )
|
Native, FEM
|
parentheses, grouping
|