About the Welding Feature
A weld joins metals by applying heat or a filler metal with a high melting point, or both. In Welding, welds and feature geometry are represented as quilts with a high level of complexity.
Consider the following about the weld feature:
• A weld feature does not change the geometry of welded components. Before you proceed to welding, make sure components to be welded have appropriate profiles.
• Adding a weld does not merge referenced components. When you retrieve a component that was welded in an assembly, its geometry remains the same.
• Welds are parametrically defined features. They are associative with the referenced geometry. They can be manipulated like other standard Creo features.
• Weld faces are represented in the assembly as quilts. A quilt represents a patchwork of connected non-solid surfaces and can consist of a single surface or a collection of surfaces.
• You cannot remove material from a weld when the feature that removes material, for example, a hole, is created in a part. Material is removed from the parent part, but the entire weld remains.
The following weld types are available:
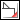 —Fillet |
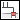 —Square groove or square butt |
 —Bevel groove or bevel butt |
 —V groove or V butt |
 —J groove or J butt |
 —U groove or U butt |
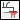 —Flare Bevel groove or Flare Bevel butt |
 —Flare V groove or Flare V butt |
 —Bevel butt with broad root face (ISO only) |
 —V butt with broad root face (ISO only) |
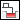 —Plug |
 —Slot |
|
 —Spot |
|
Weld Identification
Each weld feature maintains a feature ID, a weld sequence ID, a welding material, welding parameters, a weld type, and geometric references.
|
Weld Identification Format
|
Where:
|
|
# :Type_of_weld, Rod: Rod_name
|
#— The sequence ID of the weld.
Type_of_weld—The type of weld (such as, "Fillet Weld").
Rod_name—The name of a rod (such as, "Steel_001").
|
|
Example: 1:Fillet Weld, Rod: Rod1
|
 —Fillet
—Fillet —Square groove or square butt
—Square groove or square butt —Bevel groove or bevel butt
—Bevel groove or bevel butt —V groove or V butt
—V groove or V butt —J groove or J butt
—J groove or J butt —U groove or U butt
—U groove or U butt —Flare Bevel groove or Flare Bevel butt
—Flare Bevel groove or Flare Bevel butt —Flare V groove or Flare V butt
—Flare V groove or Flare V butt —Bevel butt with broad root face (ISO only)
—Bevel butt with broad root face (ISO only) —V butt with broad root face (ISO only)
—V butt with broad root face (ISO only) —Plug
—Plug —Slot
—Slot —Spot
—Spot