Reliability Without Repair
When Account for repair in reliability is cleared, the effects of repairing individual components are not considered when calculating reliability. All blocks are calculated as if they do not have any corrective maintenance or maintenance tasks.
The reliability of a single unit having an exponential failure distribution that corresponds to the constant hazard/failure rate is calculated at each time point with the equation:

Where:
R(t) = The reliability of the unit at time t.
λ = The constant failure rate.
Series System
For a series system with multiple units (say n), the reliability is given by:
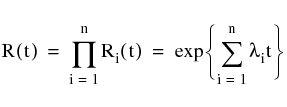
Where:
Ri(t) = The reliability of the ith unit in the series at time t.
λt = The failure rate of the ith unit in the series.
The above equation shows the series system follows the exponential distribution. The failure rate of the system is given by:

Where:
λSystem = The effective failure rate of the nth unit in the series.
Parallel System
For a parallel system with multiple units (say n), when the number of units needed for operation is 1, and a switch probability of success of 1, the reliability is given by:

When all are identical with failure rate λ, the reliability is given by:
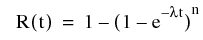
For a parallel system with identical units and a switch probability of success of 1, the reliability is given by:

Where:
λ = The failure rate of a single unit in the parallel configuration.
k = The number of units needed for operation in the parallel configuration.
n = The total number of units in the parallel configuration.
The parallel system in the RBD module is a generalized parallel system. It is equivalent to a k-out-of-n system or voting system.