Cross Product
When Cross product is selected as the calculation method, probabilities and frequencies are calculated using the summation and product terms of the cut set probabilities and frequencies using Poincare's formula.
The unavailability at a gate is calculated by using:
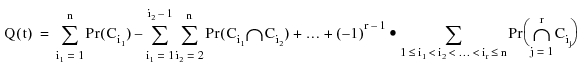

Where:
n = The order of product terms. The maximum value of n is equivalent to the total number of cut sets of the gate.
• When n = 1, this is the same as the cut set summation method.
• When n is odd, the calculated probability is greater than or equal to the actual probability.
• When n is even, the calculated probability is less than or equal to the actual probability. Thus, two successive calculations with an increasing value of n can give upper and lower bounds on the probability.
The probability of simultaneous occurrence of cut sets  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 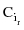 is:
is:
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 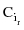 is:
is:
It is equivalent to the product of all basic events that are present in those cut sets Each basic event is considered only once.
The upper bound of the failure frequency is calculated by using:
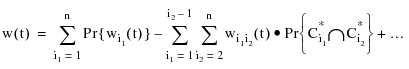
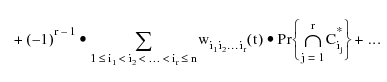
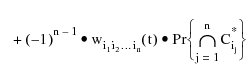
Where:
 = The frequency of an event made of common events to cut sets
= The frequency of an event made of common events to cut sets  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 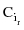 . If there are no common events for these cut sets, this quantity is set to 0. The asterisk in the cut set entry denotes the basic events of the cut sets without the common events. In the FTA module, you can select the order of product terms to use to calculate probabilities and frequencies.
. If there are no common events for these cut sets, this quantity is set to 0. The asterisk in the cut set entry denotes the basic events of the cut sets without the common events. In the FTA module, you can select the order of product terms to use to calculate probabilities and frequencies.