Model Equations
Each calculation model has its own set of equations to calculate the failure rates for the parts that it supports. Failure rate (λ) equations are based on part parameters. The parameters required by a model often include but are not limited to environment, temperature, and stress data. The values for these parameters establish Pi (π) factors, which are the variables used in the failure rate equation for the part type.
The figure below shows a MIL-HDBK-217 equation for an integrated circuit. The data for the variables in this equation is located in data tables in different sections of MIL-HDBK-217, Military Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment.
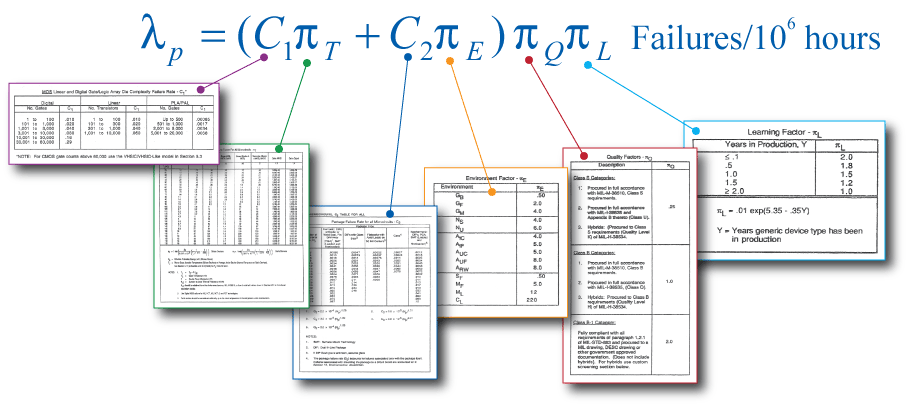
Once failure rates for individual parts have been established, a simple summation of these failure rates provides the failure rate for the next higher level assembly. A summation of the failure rates for each higher assembly level eventually results in a top-level failure rate for the entire system.
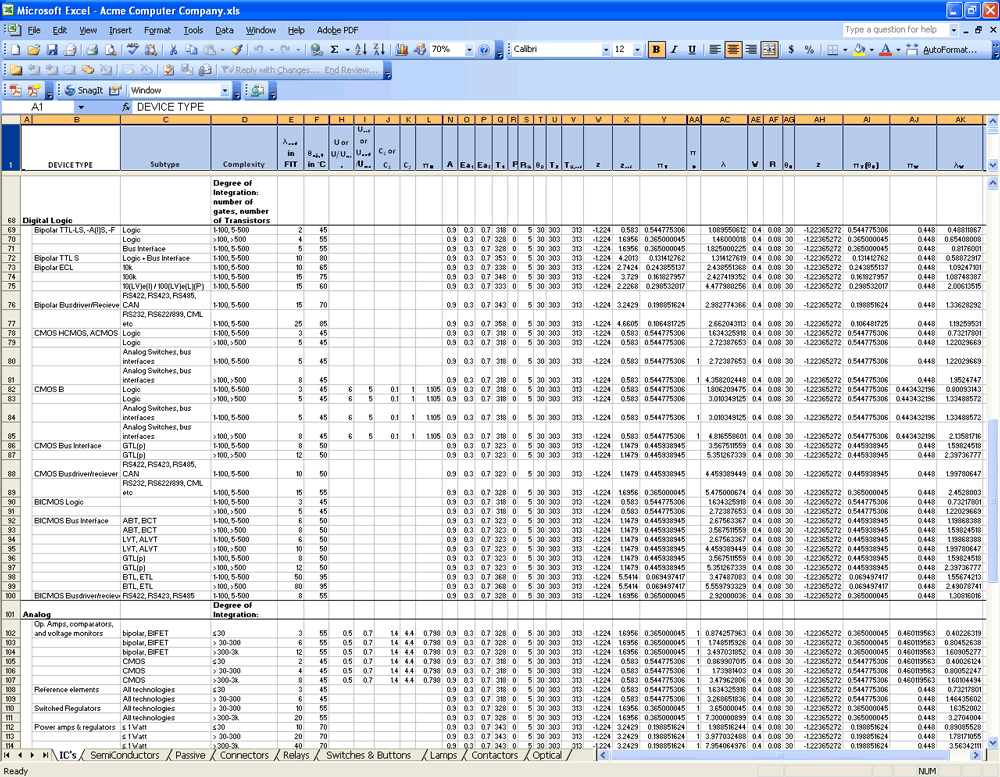
Manually calculating failure rates for parts for even a very small system is very tedious and requires great attention to detail. Small mathematical errors at the part level can be compounded at the system level. Because checking the reliability data and calculations takes nearly as much time as the original analysis, attempts to automate the process led to developing spreadsheets in which the equations for a standard are defined. The following figure shows only a portion of the data collected in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Commercial reliability prediction tools like Windchill Prediction have been specifically developed to allow efficient entry and analysis and also ensure that you can easily modify data values throughout the design process and recalculate as needed. Additionally, the failure rates calculated by a model are often used in many other types of reliability analyses. For instance, these failure rates can be used in a FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis), LCC (life cycle cost) analysis, maintainability prediction, or RBD (reliability block diagram). In Windchill Risk and Reliability, all of these different types of reliability analyses are integrated together so that the data entered and results calculated for one module can be used by other modules.