Markov Calculation Equations
The following table defines the equations for Markov calculations. General descriptions of these calculations appear in Calculation Options Page. Definitions of notations appear in Markov Equation Notations.
|
Calculation
|
Equation
|
|---|---|
|
Availability
|
 |
|
Capacity
|
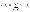 |
|
Conditional failure intensity
|
 |
|
Conditional repair intensity
|
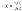 |
|
Cost per unit time
|
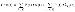 |
|
Failure density
|
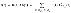 Here, Pi(t) is calculated considering that all failed states are absorbing states. |
|
Failure frequency
|
 |
|
Failure rate
|
 |
|
Frequency of departures
|
Frequency of departures from state i:  |
|
Frequency of transitions
|
Frequency of transitions from state i to state j:  |
|
Frequency of visits
|
Frequency of visits to state i:  |
|
Mean availability
|
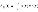 |
|
Mean capacity
|
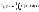 |
|
Mean cost
|
 |
|
Mean state probability
|
 |
|
Mean unavailability
|
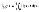 |
|
MTBF
|
 |
|
Mean time to failure, steady state OR Mean time to first failure
|
 The actual calculations are not discussed. |
|
Mean time to failure, steady state
|
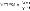 |
|
MTTR
|
 |
|
Number of departures
|
Number of departures from state i:  |
|
Number of failures
|
Number of failures from state i: 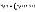 |
|
Number of repairs
|
Number of repairs from state i:  |
|
Number of transitions
|
Number of transitions from state i to state j:  |
|
Number of visits
|
Number of visits to state i:  |
|
Reliability
|
 Here, Pi(t) is calculated considering that all failed states are absorbing states. |
|
Repair frequency
|
 |
|
State probability
|
Individual state probabilities are calculated using information given in the Markov diagram. The probability of state i at time t, Pi(t), is calculated using the transition matrix and the initial state vector by the Fourth-Order Runge-Kutta Method. The error tolerance, ∈, is used to obtain the desired accuracy and stop the iterations. If ∈ is very small, then the computational time will be high; however, providing that round-off errors are negligible, results will be more accurate. If the system is repairable, then steady state results of individual state probabilities are calculated by solving a set of linear equations that correspond to the steady state behavior of the system.
|
|
Time spent in state
|
 |
|
Total capacity
|
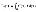 |
|
Total cost
|
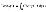 |
|
Total downtime
|
 |
|
Total uptime
|
 |
|
Unavailability
|
 |
|
Unreliability
|
 |