About Redline
In the typical change notice process, detailed plans are prepared for the objects that need modification and solutions are worked out in the next resulting object revisions. Since some changes can require significant time to validate and process, this can lead to challenges when other change notices need to make modifications to the same affected objects that are already being modified. In some cases, the modifications in the next resulting revisions are backed out so that these other changes can pass through, or changes may get released out of revision order so that these other changes can be accommodated.
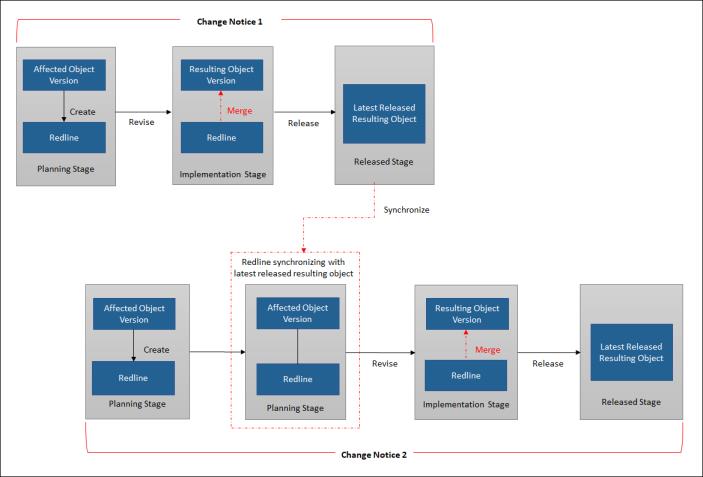
Using the redline feature, multiple users can plan changes to the same affected objects concurrently without committing to the next sequential revision. In the planning stage of the change notice, a redline is created on the latest released affected object instead of creating the next resulting object version. The redline product structure browser can be launched to plan changes that are automatically tracked with visual indicators. You can continue working on the redline until the implementation planning is complete. When the implementation stage starts, the planned redline changes are merged when the next revisions are created using the revise action from within the change context. Once the change notice is released, the modifications in the resulting objects are synchronized with the latest redlines of other open change notices that are currently being planned.
The redline feature provides ability to:
• Create a set of suggested changes in a product structure (such as inserting or removing parts) that are automatically highlighted using visual indicators such as old entries (strikethrough).
• Complement existing revision methods by providing the flexibility to use parallel redline planning methods with improved visibility to concurrent changes.
• Automatically keep open redlines up to date as other changes are released or appropriately mark redlines as suspect when conflicting changes are detected that require manual reconciliation.
Best Practice for Redline
Use the redline as part of the up-front planning process to define changes that will not interfere with other changes. You can modify the existing redlines based on the permission to the change task and the redline, and prior to the creation of the next sequential revision.
Explicitly start the execution of the change notice to implement the changes. When the change notice starts execution, all redlines should be approved and the creation of new redlines should not be permitted.
Because some change management processes allow the creation of the resulting objects prior to the execution stage, the existence of at least one resulting object on the change task will also prevent the creation of a new redline.
Related Topics