|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
StandardUIComponentValidation Service
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as the validation service. This is the service class that controls UI Validation. It receives validation requests from the client infrastructure and delegates to the appropriate validators and filters for validation results. It then passes the validation results back to the client infrastructure.
Customizers and application developers should not have to interact directly with this class.
|
|
UIValidationKey
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as a validation key. A UIValidationKey is used to identify the UI Component being validated. You can think of a UIValidationKey as having a one-to-one relationship with an action or attribute.
|
|
UIValidationCriteria
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as the validation criteria.
The UIValidationCriteria is a bean class that contains the context (request, session) data which is passed from the client infrastructure to the validators and filters via the validation service.
Most of the content in the UIValidationCriteria is taken directly from the NmCommandBean, although the objects are typically returned as WTReferences, as opposed to NmOids.
|
|
UIValidationResult
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as a validation result.
A UIValidationResult represents one unit of validation. In other words, it associates a validation status with a UI Component (action or attribute). In cases where validation is being performed for the same action on multiple objects, a UIValidationResult can be associated with each object.
|
|
UIValidationResultSet
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as a result set.
A UIValidationResultSet is just a collection of UIValidationResult objects. The result sets are used in situations where multiple validations are being performed at the same time. For example, if a validator was doing a pre-validation check for the same action on multiple objects, it could aggregate the validation results for each of the objects into a UIValidationResultSet.
|
|
UIValidationStatus
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as validation status.
This is an enumeration used to determine if or how a UI component should be displayed in the UI. For example, there are values to indicate that an action should be hidden, that an action should be disabled, or that an action should be enabled.
|
|
UIValidationFeedbackMsg
|
Java class
|
Often referred to as a feedback message.
This is a message that can be associated with a validation result. It is only used for post-select validation and post-submit validation. Any feedback messages associated with validation results returned by pre-validation will be ignored.
Feedback messages can have different feedback types (FeedbackType.java) associated with them to indicate whether they are, for example, error messages, warning messages, or info messages.
|
|
UIComponentValidator
|
Java interface
|
This is the interface that all validator implementations need to implement. However, validators should not directly implement this interface. Rather, they should extend DefaultUIComponentValidator.
Each UI component can have zero or one validators associated with it. Typically, a validator will contain logic specific to a single UI component. For more generic validation logic that applies to multiple UI components, a filter is typically used.
Validators are called by the validation service to determine the validation status for a specific UI component.
Customizers and application developers should not have to interact directly with this class.
|
|
DefaultUIComponentValidator
|
Java class
|
This is a default implementation of the UIComponentValidator interface. All validator implementations should extend this class.
|
|
ValidationFilter
|
Java interface
|
This is the interface that all filter implementations need to implement. However, filters should not implement this interface directly. Rather, they should extend DefaultSimpleValidationFilter or DefaultUniversalValidationFilter.
Each UI component can have zero to many filters associated with it. Typically, a filter will contain generic validation logic that could apply to multiple UI components. For validation logic that is specific to a single UI component or a small set of UI components, a validator is typically used.
There are two categories of filters: simple filters and universal filters. Simple filters are applied on a component-by-component basis. In other words, you have to choose which UI components the logic in a simple filter will apply to. Conversely, universal filters are applied to all UI components, which means you have to choose which UI components the logic in a universal filter does not apply to.
Filtersare called by the validation service to determine the validation status for a specific UI component.
Customizers and application developers should not have to interact directly with this class.
|
|
SimpleValidationFilter
|
Java interface
|
This is the interface that all simple filter implementations need to implement. However, simple filters should not implement this interface directly. Rather, they should extend DefaultSimpleValidationFilter.
Customizers and application developers should not have to interact directly with this class.
|
|
UniversalValidationFilter
|
Java interface
|
This is the interface that all universal filter implementations need to implement. However, universal filters should not implement this interface directly. Rather, they should extend DefaultUniversalValidationFilter.
Customizers and application developers should not have to interact directly with this class.
|
|
DefaultSimpleValidationFilter
|
Java class
|
This is a default implementation of the SimpleValidationFilter interface. All simple filter implementations should extend this class.
|
|
DefaultUniversalValidationFilter
|
Java class
|
This is a default implementation of the UniversalValidationFilter interface. All universal filter implementations should extend this class.
|
|
UIComponentSolutionGroup
|
Java interface
|
This is an interface that all solution group implementations need to implement.
A solution group is a special type of validator that is used for pre-validation based on the installed solutions. For example, if a given action should not be available if Windchill ProjectLink is not installed, that logic should be defined in a solution group.
|
|
*actions.xml
|
XML file(s)
|
There are multiple “satellite” versions of actions.xml files (typically one per module), which contain action definitions.
It is also in these files that we configure actions to include simple filters, and exclude universal filters.
|
|
*service.properties.xconf
|
XConf file(s)
|
There are multiple “satellite” versions of service.properites.xconf files (typically one or more per module), which contain class delegate registry entries.
These files are where you register your validators, filters and solution groups so that the validation service knows where to find them.
|

Key |
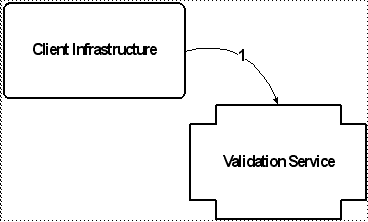
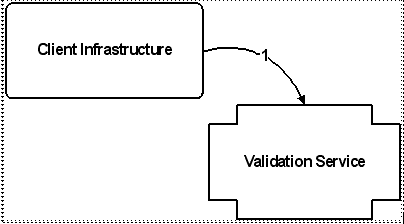
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). |
Key |
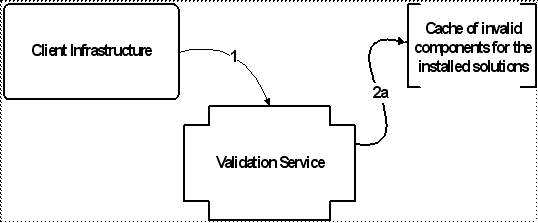
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. For each validation key, the validation service performs a series of tasks to determine the validation status for that key. The tasks are executed in the following order: a. Check to see if the validation key is in the list of invalid keys for the installed solution set. |
Key |
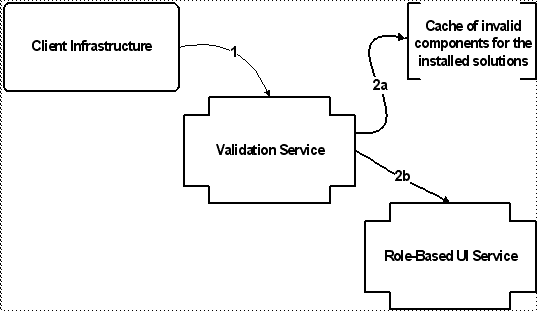
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. For each validation key, the validation service performs a series of tasks to determine the validation status for that key. The tasks are executed in the following order: a. Check to see if the validation key is in the list of invalid keys for the installed solution set. b. Check to see if the role-based UI service was configured to disable or hide the component. |
Key |
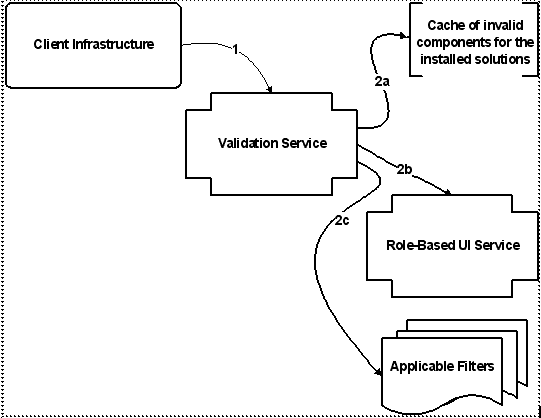
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. For each validation key, the validation service performs a series of tasks to determine the validation status for that key. The tasks are executed in the following order: a. Check to see if the validation key is in the list of invalid keys for the installed solution set. b. Check to see if the role-based UI service was configured to disable or hide the component. c. Check to see if any of the filters associated with the UI component indicate that the component should be disabled or hidden. |
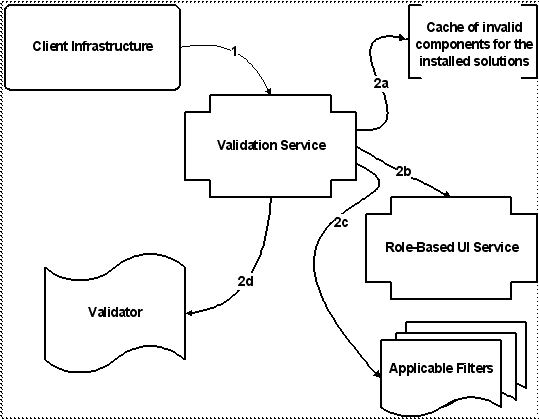
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. For each validation key, the validation service performs a series of tasks to determine the validation status for that key. The tasks are executed in the following order: a. Check to see if the validation key is in the list of invalid keys for the installed solution set. b. Check to see if the role-based UI service was configured to disable or hide the component. c. Check to see if any of the filters associated with the UI component indicate that the component should be disabled or hidden. d. Get the validation status from the validator, if there is one associated with the UI component. |
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. For each validation key, the validation service performs a series of tasks to determine the validation status for that key. The tasks are executed in the following order: a. Check to see if the validation key is in the list of invalid keys for the installed solution set. b. Check to see if the role-based UI service was configured to disable or hide the component. c. Check to see if any of the filters associated with the UI component indicate that the component should be disabled or hidden. d. Get the validation status from the validator, if there is one associated with the UI component. 3. Return the validation result or validation result set to the client infrastructure. |
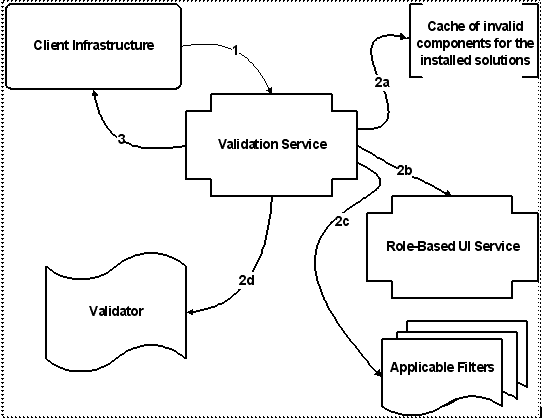
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). |
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. The validation service checks to see if there is a validator associated with the action. If so, it calls the validator to get the validation status (permitted or denied) for the action. |
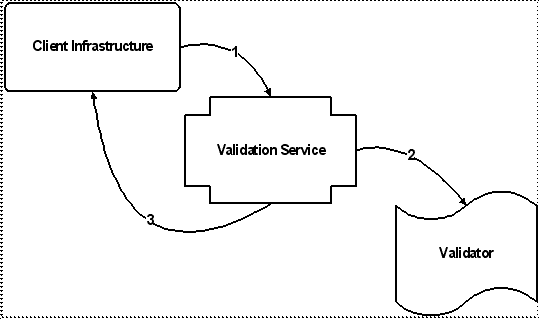
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. The validation service checks to see if there is a validator associated with the action. If so, it calls the validator to get the validation status (permitted or denied) for the action. 3. The validation service passes the validation status (wrapped in a validation result) from the validator to the client infrastructure, which either displays the target page/wizard, or brings the user back to the page where the action was invoked. |
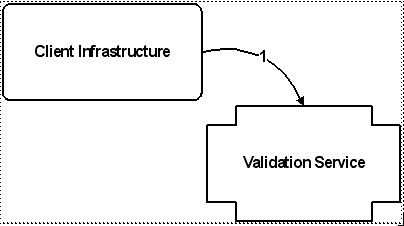
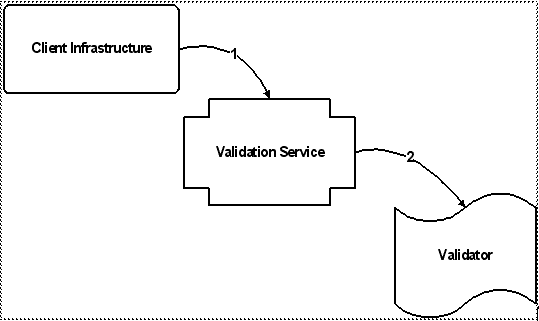
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an id associated with a wizard's "Next" or "OK" action (represented by a validation key), and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). |
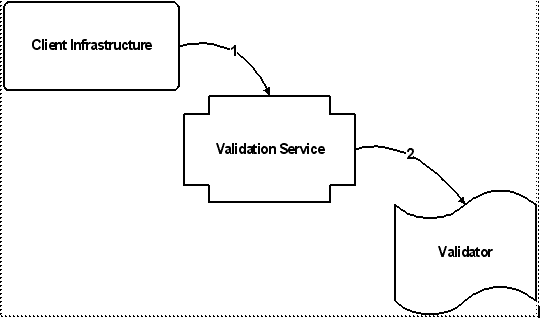
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an id associated with a wizard's next or OK action (represented by a validation key), and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. The validation service checks to see if there is a validator associated with the "Next" or "OK" action. If so, it calls the validator to get the validation status (permitted or denied) for the action. |
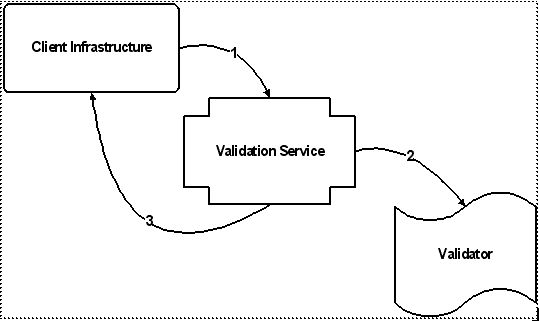
Key |
1. The Client Infrastructure calls the validation service, passing an action (represented by a validation key) corresponding to the page being rendered, and the context data (represented by a validation criteria instance). 2. The validation service checks to see if there is a validator associated with the "Next" or "OK" action. If so, it calls the validator to get the validation status (permitted or denied) for the action. 3. The validation service passes the validation status (wrapped in a validation result) from the validator to the client infrastructure, which either allows the user to proceed to the next step in the wizard or submit the entire wizard, or brings the user back to the wizard step where the action was invoked. |