Import Classification Structure from CSV File
To import a classification structure, the classification structure must be outlined in an XML file. You can modify the XML file prior to import, but if your structure is complex, this is not easily done.
Instead, it is much easier to manage a CSV file. When you are ready to import the structure, you can use the CSVToXMLGenerator utility to transform the CSV file to an importable XML file.
|
|
PTC recommends that you use this utility when creating an initial classification structure. You should not use this utility to update an existing structure. Any data in the existing structure that is not represented in the CSV file is overwritten and consequently removed.
|
To transform a CSV file to XML, execute the following command from a Windchill shell:
Windchill com.ptc.windchill.csm.csvtoxml.CSVToXMLGenerator <path to CSV file> -verbose
where:
• <path to CSV file> is the path to the CSV file on your local machine.
• The verbose parameter is optional and should be used for debugging purposes.
The XML file is generated with the same name and in the same location as the CSV file.
Before You Begin
• The Windchill server does not need to be running to use the CSVToXMLGenerator utility.
• The imported CSV file must be in a unique format. This is not the same format as the CSV file that is generated using the Export to CSV action available from the Classification Tree table.
• Before loading the resulting XML file, the following should already exist in Windchill. (This is not the case when importing an exported ZIP or JAR file.)
◦ Global enumerations
◦ Reusable attributes
◦ Quantities of measure
• To import the generated XML file, compress it in a ZIP file. From the Classification Tree, select > .
Import Errors and Supported Values
Data validation occurs when you import the file to Windchill. If the XML file includes invalid data or values, you receive an error during the import operation.
While it is easier to work with a CSV file, the format accepted by the CSVToXMLGenerator utility includes several limitations. For example, you cannot import schematics or images. You also cannot specify autonaming rules.
If an attribute or constraint is not listed in the tables below, it is not supported and causes an error during import.
CSV Formatting Rules
• Single values containing a comma must be enclosed inside a double quote. For example:
Hong Kong, Berlin, "New York, NY", London
• Escape a double quote with a double quote. For example:
Parts available in the ""Drive System"" catalog
Node and Attribute Shared Columns
There are 7 columns that contain either node or attribute information. These columns use the following format:
Node/Attribute
The title before the slash refers to classification nodes; the title after the slash refers to classification attributes.
|
Column Name
|
Node Value
|
Attribute Value
|
|
Node/Attribute
|
This column identifies the row as containing a classification node or a classification attribute.
Enter one of the following values:
• Node
• Attribute
|
|
ParentIntName/NodeIntName
|
Internal name of the parent node.
|
|
Use NULL to identify the root node.
|
|
Internal name of the node for which the attribute is being defined.
|
|
NodeIntName/AttributeIntName
|
Internal name of the node.
|
Internal name of the attribute.
|
|
DisplayName/DisplayName
|
Display name of the node.
|
Display name of the attribute.
|
|
Description/IBAName
|
Value to enter in the Description field for the node.
|
Reusable attribute name.
|
|
Keywords/DataType
|
Value to enter in the Keywords field for the node.
|
The data type of the attribute.
The following values are accepted:
wt.units.FloatingPointWithUnits
java.lang.Boolean
java.sql.Timestamp
java.lang.Long
java.lang.String
com.ptc.core.meta.common.Hyperlink
com.ptc.core.meta.common.FloatingPoint
|
|
Namespace
|
Name set for a namespace
|
|
|
IsInstantiable/Description
|
Value to enter in the Instantiable field for the node.
The following values are accepted:
TRUE
FALSE
|
Value to enter in the Description field for the attribute.
|
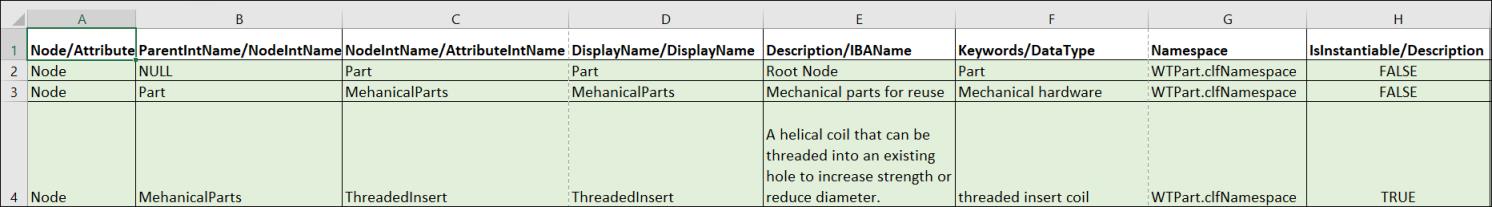
For example, you create a CSV file with the following values in “Node” rows:
| The arrangement of columns in the CSV file must be same as shown on the screenshot above. |
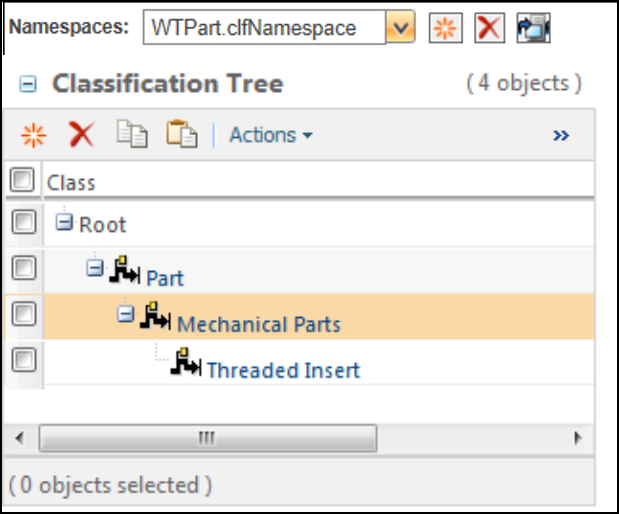
After the CSV is converted to XML and imported, this is the resulting structure:
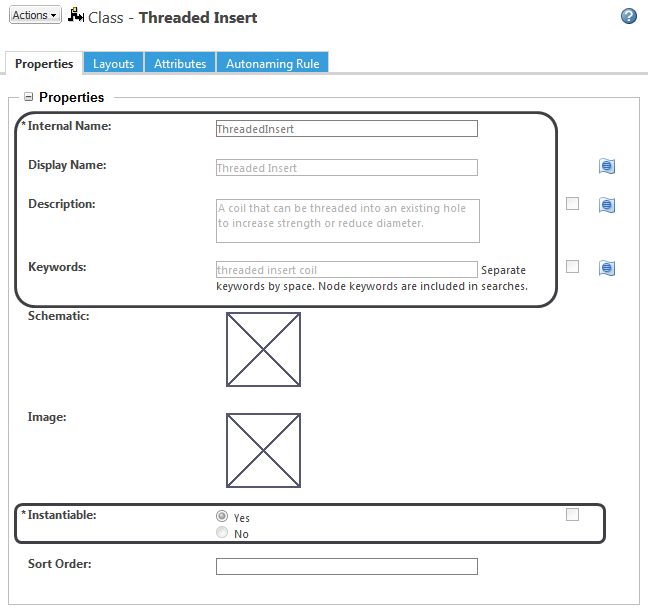
The “Threaded Insert” node has the following values defined:
Attribute Columns
The following columns are only applicable to “Attribute” rows:
Column Name | Accepted Values |
DefaultValue | Default value for the attribute. For multiple default values, use a comma separated list. For example: 0.0 m, 1.5 m http://google.com(Google), http://ptc.com(PTC) |
IsSingleValued | Specify whether the attribute has a single value. Accepted values: TRUE FALSE |
IsRequired | Specify whether the attribute is required. Accepted values: TRUE FALSE |
StringLength | For string values, specify a length constraint. Use the following format: [lower limit, upper limit] For example: [2,5]—String must be between 2 and 5 characters [NULL,50]—String cannot be more than 50 characters [10,NULL]—String must be at least 10 characters |
Lowercase | Convert uppercase characters to lowercase. Accepted values: TRUE FALSE |
Uppercase | Convert lowercase characters to uppercase. Accepted values: TRUE FALSE |
LegalValueList | A list of accepted values. Separate values using a pipe character (“|”). For example: 1.0 m|1.5 m|2.0 m Copper|Aluminum|Steel |
EnumeratedList | Enumerated value list. You can provide a local or global enumerated value list. Local enumeration constraints use the following format: LOCAL##<sort type>##<internal name>##<display_name>~~<internal_name>##<display_name> where: • <sort_type>—The sort type value is Automatic_Sort or Manual_Sort. • <internal name>##<display name>—Identify the internal name and display name of the enumeration entry. • ~~ —Use two tilde characters to separate multiple entries. For example: LOCAL##Manual_Sort##red1##Light Red~~red2##Dark Red~~green1##Light Green Global enumeration constraints use the following format: GLOBAL##<enumeration>##<parent enumeration>##<organization>##<organizer name>##/<domain> where: • <enumeration>—The internal name of the enumeration. • <parent enumeration>—If the enumeration is a sub-enumeration, specify the internal name of its parent enumeration. If the enumeration does not have a parent enumeration, leave this field blank. • <organization>—The Owning Organization value for the enumeration. • <organizer name>—The internal name of the organizer that holds the enumeration. • /<domain>—The Domain value for the enumeration. For example: GLOBAL##Countries##LocaleCodes##Site##Org_Locales##/System GLOBAL##LocaleCodes####Site##Org_Locales##/System | The sort order specified for the global enumeration is used as the default sort order. |
|
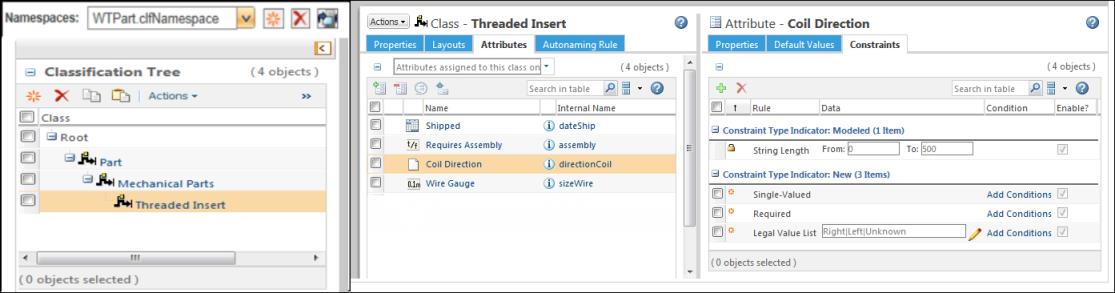
For example, you create a CSV file with the following values in “Attribute” rows:
| The arrangement of columns in the CSV file must be same as shown on the screenshot above. |
The “Threaded Insert” node has the following attributes defined: