Mapping Attributes and Parameters
In order to set up the parameters so that they are published in the authoring application user interface, the administrator maps them in the
Type and Attribute Management utility. For more information on the
Type and Attribute Management utility, refer to
Basic Administration located at
PTC Reference Documents.
The following list provides information about case-sensitivity when setting up authoring application parameters that need to be recognized in Windchill:
• Windchill is case-sensitive in its handling of attributes; but not all authoring applications are.
• If the authoring application does not support case-sensitive attribute names, then they should be handled as the value in all upper case characters, regardless of how they are shown in the authoring application.
• The Windchill global attribute Name is case-sensitive; therefore, when creating an global attribute to map to an authoring application parameter that does not support case-sensitive attributes, the name must be in all uppercase characters or the administrator must explicitly map the name of the global attribute to the name of the CAD parameter.
• Your authoring application does not support case-sensitive parameters; however, it does support mixed-case parameters. This means that the user cannot create a parameter named Cost or COST, but the user can type COST, Cost, or cost.
The administrator sets up an attribute on the authoring application side in the Properties window. Then, in Windchill, under > > , the administrator maps this attribute. Use the following process to map attributes and parameters:
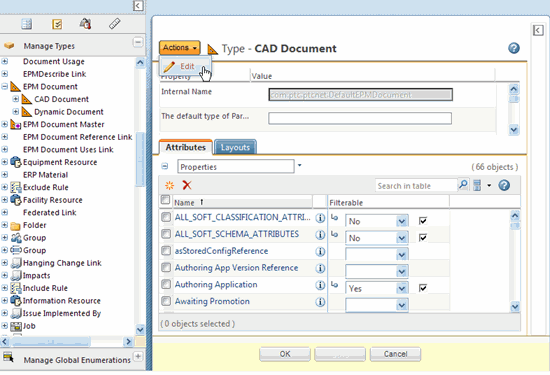
1. Check out CAD Document subtype using the following steps.
a. From Manage Types, expand the EPM Document subtype.
b. Select CAD Document.
c. From actions, select the Edit icon. The CAD Document subtype is checked out, as shown in the following figure.
2. Use the following steps to create a new attribute.
a. Click the New Attribute icon on the Attributes tab. The New Attribute window is comprised of three steps:
a. Define Attributes
b. Select Global Attribute
c. Set Properties
b. To Define Attributes:
a. Specify an Internal Name for the object. This is a required field.
b. Select the attribute Type from the list of attributes. For example,
▪ Global—Global attributes can have zero or more values for an attribute. In previous releases, global attributes were known as instance-based attributes. The global attribute set is created using the Manage Global Attributes window.
▪ Alias—Alias attributes are an alias for an attribute on a related object. They can have zero to many values.
▪ Calculated—Calculated attributes are derived from the values of other attributes using formulas. They can have zero to many values.
c. To select the Global Attribute:
a. Specify an Internal Name for the object. This is a required field.
b. Select the attribute Type from the list of attributes. For example,
▪ Global—Global attributes can have zero or more values for an attribute. In previous releases, global attributes were known as instance-based attributes. The global attribute set is created using the Manage Global Attributes window.
▪ Alias—Alias attributes are an alias for an attribute on a related object. They can have zero to many values.
▪ Calculated—Calculated attributes are derived from the values of other attributes using formulas. They can have zero to many values.
d. To set properties, enter the property values for the attribute.
The available properties differ depending on the combination of attribute type and data type, or depending on the global attribute definition. Certain properties are required and must be specified before the attribute can be created. Most properties on an attribute can be specified or edited on the attribute information page after the attribute is created.
3. To map the attribute in Windchill, complete the following steps:
a. Click the information icon next to the attribute you want mapped.
b. Enter the desired value next to the authoring application you want the attribute mapped against.
c. Save your updates.