Equivalent Usages
An equivalent usage is used to relate a usage path of a part in an upstream context to a usage path of its equivalent part in the downstream context. Equivalent usage links are always created between upstream part usages and their respective equivalent downstream part usages. You can monitor discrepancies between exact equivalent usages in cases where the upstream usage is overloaded and consumed at various places in the downstream structure.
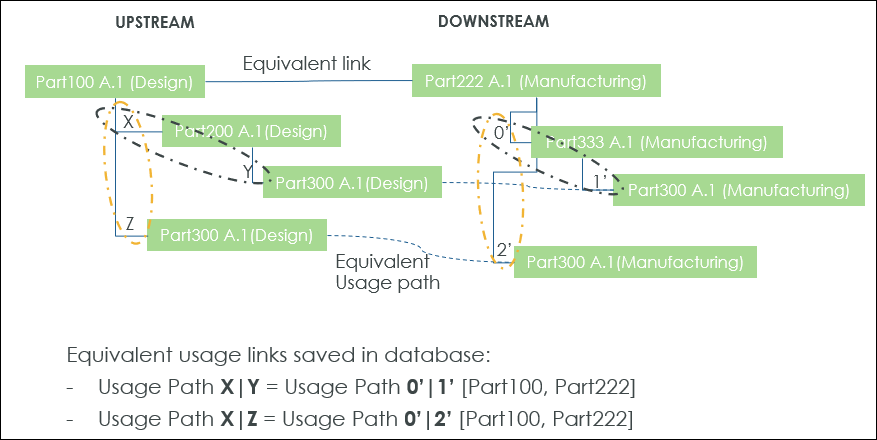
In the above example, BOM Transformer is considered to be in the usage mode. The example illustrates equivalent usage between the upstream and downstream structure.
• Upstream Part100 (Design) is equivalent to the downstream Part222 (Manufacturing).
• Path between Part100 (Design) and Part300 (Design) is saved as a usage path, that is X|Y.
• Path between Part222 (Manufacturing) and Part300 (Manufacturing) is also saved as a usage path, that is 0’|1’.
• The two usage paths are linked together as an equivalent usage link.
Equivalent usage status is visible only in the usage mode. To view the latest status, in the middle pane tool bar, click  . You need to execute the action to view the latest status whenever the structure is updated.
. You need to execute the action to view the latest status whenever the structure is updated.
 . You need to execute the action to view the latest status whenever the structure is updated.
. You need to execute the action to view the latest status whenever the structure is updated.Status indicators take longer to update in cache mode than noncache mode. |
The following indicators display the equivalent usage status:
Status | Description |
|---|---|
 | Equivalent usage is fully consumed. |
 | Equivalent usage does not exist. |
 | Equivalent usage is reused from the upstream assembly. |
 | Equivalent usage information has not been retrieved. |
 | Equivalent usage link exists but the equivalent usage cannot be located. |
 | Equivalent usage exists but the link is unresolved. |
 | Equivalent usage is under consumed. |
 | Equivalent usage is over consumed. |
 | Equivalent usage exists but equivalent usage status is unknown. |
• The equivalent usage status appears only for the parts that are currently visible in the upstream and downstream structure. • The equivalent usage status is blank when you refresh the upstream or downstream structure. • In the case of one-to-many equivalent usage links, if one of the usages is consumed and others are broken or in different context, the status shows  . .• In the case of one-to-one equivalent usage link, if the link is broken from either side, the status shows  on the other side. on the other side.• In the case of one-to-one equivalent usage path, if the path is under different context, the status shows  . This status appears only when the Enable Structure Cache preference is enabled. If the preference is disabled, the status shows . This status appears only when the Enable Structure Cache preference is enabled. If the preference is disabled, the status shows  . . |
Equivalent usage links are maintained when you perform the following actions:
• Cut or Paste in downstream
• Drag from upstream to downstream
• Remove Selected Assembly and Move Up Child Parts
In the upstream structure, if you cut or drag an equivalent usage on another upstream part, the equivalent usage link breaks. |