Configuration Management Objects: Windchill Parts
Windchill Aerospace & Defense Configuration Items and Design Solutions configuration management methodology uses Windchill parts (WTParts) to manage object types, relationships, and functionality.
Part Types
The Windchill Aerospace & Defense configuration management methodology uses out-of-the-box part types that include all of the properties and attributes that facilitate the product configuration management of Windchill Aerospace & Defense Setup for Configuration Items and Design Solutions (CIDSCFG).
The following is a list of the out-of-the-box part types:
• Base Upper Level Part
• Base Configuration Item
• Base Link Object
• Base Design Solution
• Base Lower Level Part
|
|
CIDSCFG supports the Link Object out of the box, but additional configuration is necessary. For more information, see Configuring the System to Employ the Link Object.
|
These part types are not instantiable. This means that when you create a new part, you cannot assign it one of the base types. Rather, subtypes represent the actual business objects being managed. Subtypes are children of the base part types and inherit the necessary properties and attributes.
When you create a new part, you select one of the instantiable subtypes to assign to the new part from the Type menu in the New Part window. The subtype determines the necessary properties and attributes for that part. For example, if you are creating a new lower-level part, you select > . The Lower Level Part subtype has inherited properties and attributes from the Base Lower Level Part type and passes those properties and attributes to the new part.
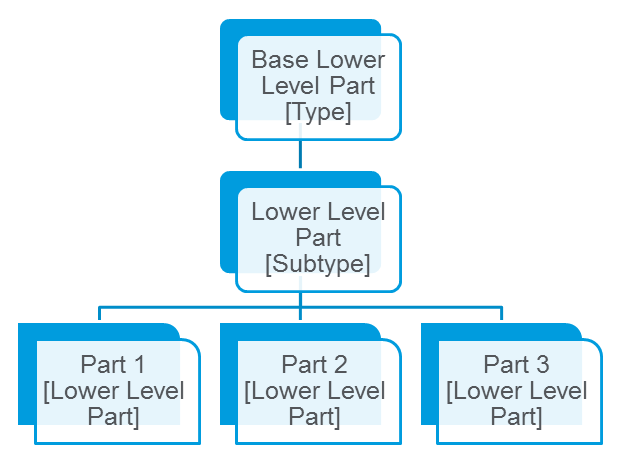
Part Subtypes
Subtypes of the base part types are instantiable. They are used to create and manage actual business objects. Subtypes have structure-level properties and relationship constraints that the system uses to identify their place in the product structure and their role in the configuration management process. You can use the out-of-the-box part subtypes or create your own subtypes to fit the needs of your site.
Structure Level Property
Part subtypes use the Structure Level property to identify where they fit in the product structure. The Structure Level property indicates how the system should treat the part type. For example, certain actions, tabs, and tables are visible only to part types with certain structure-level property values.
The following Structure Level property values are available:
• <blank>
• Configuration Item
• Link Object
• Design Solution
• Lower Level Part
A structure-level property of <blank> is selected for upper level parts. This value also allows the subtype to be subtypeable, which means subtypes can be created for it. |
Relationship Constraints
Relationship constraints define the relationship between objects. For example, if using out-of-the-box part subtypes, relationship constraints specify that only an upper-level part can be the parent of a configuration item. The following table outlines the pre-configured relationship constraints for the out-of-the-box part subtypes:
Parent Part Type | Child Part Type |
|---|---|
Upper Level Part | Upper Level Part |
Upper Level Part | Configuration Item |
Configuration Item | Design Solution |
Design Solution | Lower Level Part |
Lower Level Part | Lower Level Part |
You can also define relationship constraints for custom part subtypes. For example, if you create two upper-level part subtypes, “Zone” and “Section,” then you can specify that a zone is the only part that can be the parent of a section and that a section is the only part that can be the parent of a configuration item.
Although administrators can create new relationship constraints for part subtypes, the system uses structure-level properties to ensure that the Windchill Aerospace & Defense configuration management product structure remains intact. For example, an administrator cannot create a relationship constraint that specifies a part subtype with a structurelevel property of Lower Level Part as the parent of a part subtype with a structure-level property of Configuration Item. |
For more information, see Custom Part Subtype Examples.
For more information about managing relationship constraints, see Defining Part Subtypes and Relationship Constraints.
Out-of-the-Box Part Subtypes
Windchill Aerospace & Defense is delivered with the following out-of-the-box part subtypes:
• Upper Level Part
• Configuration Item
• Link Object
• Design Solution
• Lower Level Part
Upper Level Part Subtype
The out-of-the-box Upper Level Part subtype is the highest level in the product structure. Parts of this type can have a child part with a type of Upper Level Part or Configuration Item.
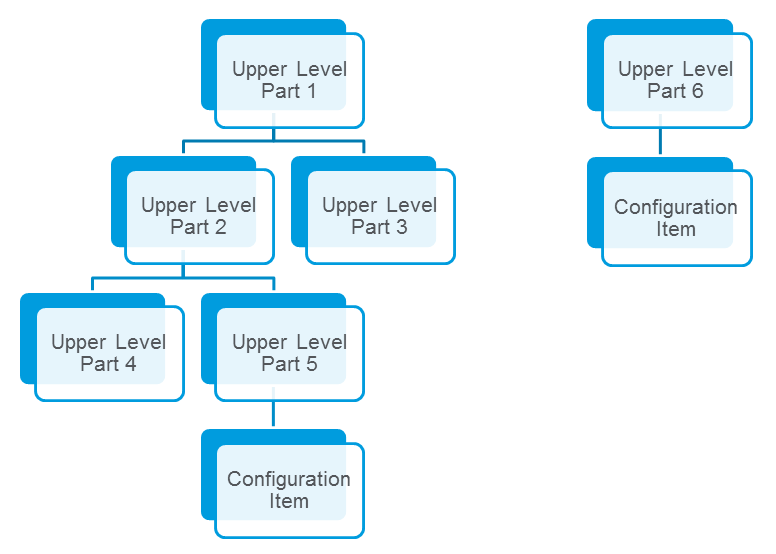
Configuration Level Subtypes
The configuration level has three out-of-the-box subtypes: Configuration Item, Design Solution, and Link Object. Out of the box, Windchill Aerospace & Defense Configuration Items and Design Solutions is configured to use the Configuration Item-Design Solution (CI-DS) model for the configuration level. CIDSCFG supports the Link Object type out of the box, but additional configuration is necessary. For more information about the link object, see Configuration Level Structure with the Link Object.
Using the CI-DS model, the configuration level part subtypes are configured as follows:
• Configuration Item—A part with a type of Configuration Item can only have a parent with a the Upper Level Part part type and a child with the Design Solution part type.
• Design Solution—A part with a type of Design Solution can only have a parent with the Configuration Item type and a child with the Lower Level Part type.
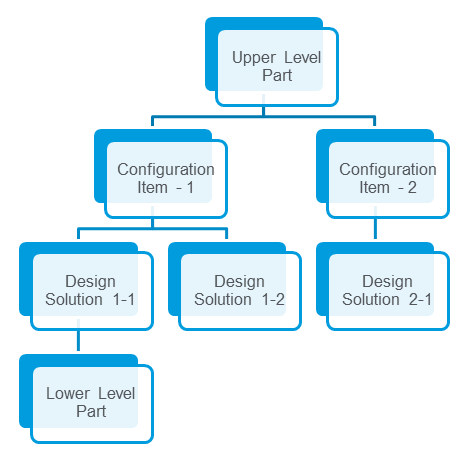
Custom Part Subtypes
You can create custom part subtypes to fit the needs of your site. These new part subtypes must use appropriate structure-level properties, and the relationship constraints you define must be allowed by the Windchill Aerospace & Defense configuration management methodology. For example, you cannot create a part subtype with a structure-level property of Lower Level Part and define a relationship constraint allowing this part subtype to have a child subtype with a structure-level property of Configuration Item. For more information, see Defining Part Subtypes and Relationship Constraints.