Mapped Attributes
Overview
Mapped attributes are used to facilitate planning in PTC FlexPLM. This functionality enables users to define what products to offer for a given season. For example, a company might want to offer five different sweaters for the winter season.
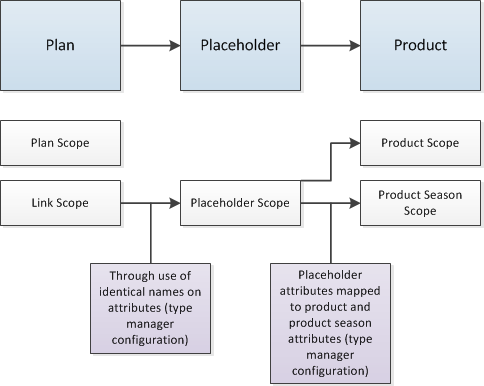
When product line managers create a plan, they can create placeholders. Placeholders are intended product offerings generated from the plan. The placeholder captures what is needed by the merchant. It acts as a way to communicate requirements with designers, developers, sourcing managers, material managers, and so on. A placeholder represents each line item in the plan. For example, each sweater offered in a season is a line item. Each sweater could have a different price point, color selection, fabric, design, gender, or other characteristics. These characteristics are represented by attributes.
Mapped attributes enable administrators to configure attributes on a product. Those attributes from the product are mapped to a placeholder. When a product is created for a placeholder, that attribute can be automatically populated, and the values are equivalent to those on the placeholder.
Data originates with a plan. The data is inherited by placeholders, and it is ultimately inherited by products.
In the user interface, the mapped attribute appears on the placeholder. When users create a product on that placeholder, the mapped attribute automatically appears on the product, using the same attribute value they selected on the placeholder.
The value is locked and cannot be changed. This prevents users from associating products where the mapped attributes are not the same (for example, you would not want to associate sweatpants to a sweater).
Creating a Mapped Attribute
Follow these instructions to create a mapped attribute. For instructions on creating a mapped attribute from a single list, see Creating a Mapped Attribute for a Single List Attribute Type. For instructions on creating a mapped attribute from a reference, see Creating a Mapped Attribute for a Reference or Reference List Attribute Type.
2. Navigate to the Product type and create a new attribute with the same display name (for example, Gender).
| This attribute can be created on the Product type or any of its subtypes. |
◦ Enter a unique name in the Internal Name field. This field must be unique for each attribute on a type and its synchronized types.
◦ For the Type, Data Type, and FlexPLM Attribute Type, select the same types as the placeholder attribute (for example, local, string, and text).
◦ From the Mapped Attribute list, select the attribute you just created.
3. After you click Finish, the attribute on the product is mapped to the attribute on the placeholder.
Creating a Mapped Attribute for a Single List Attribute Type
Follow these instructions to create a mapped attribute for a single list.
2. Navigate to the Product type and create a new attribute (for example, Gender).
| This attribute can be created on the Product type or any of its subtypes. |
a. Enter a unique name in the Internal Name field. This field must be unique for each attribute on a type and its synchronized types.
b. For the Type, Data Type, and FlexPLM Attribute Type, select the same types as the placeholder attribute (for example, local, string, and single list).
c. Do not select an attribute from the Mapped Attribute list. If you select an attribute, an error message appears.
d. Click Finish to save the attribute.
e. Add an enumerated value list constraint using a global enumerated value list. The enumerated value list on the Product type must match the enumerated value list in the attribute on the Placeholder type.
f. Click the attribute to reload it.
g. From the Mapped Attribute list, select the attribute you created on the Product type.
h. Save the attribute. The attribute on the product is mapped to the attribute on the placeholder.
Creating a Mapped Attribute for a Reference or Reference List Attribute Type
Follow these instructions to create a mapped attribute for a reference.
2. Navigate to the Product type and create a new attribute with the same display name.
| This attribute can be created on the Product type or any of its subtypes. |
a. Enter a unique name in the Internal Name field. This field must be unique for each attribute on a type and its synchronized types.
b. For the Type, Data Type, and FlexPLM Attribute Type, select the same types as the placeholder attribute (for example, local, string, and single list).
c. Do not select an attribute from the Mapped Attribute list. If you select an attribute, an error message appears.
d. Click Finish to save the attribute.
e. Add an enumerated value list constraint using a global enumerated value list. The enumerated value list on the Product type must match the enumerated value list in the attribute on the Placeholder type.
f. Click the attribute to reload it.
h. From the Mapped Attribute list, select the attribute you created on the Product type.
i. Save the attribute. The attribute on the product is mapped to the attribute on the placeholder.