Cross-Site Request Forgery
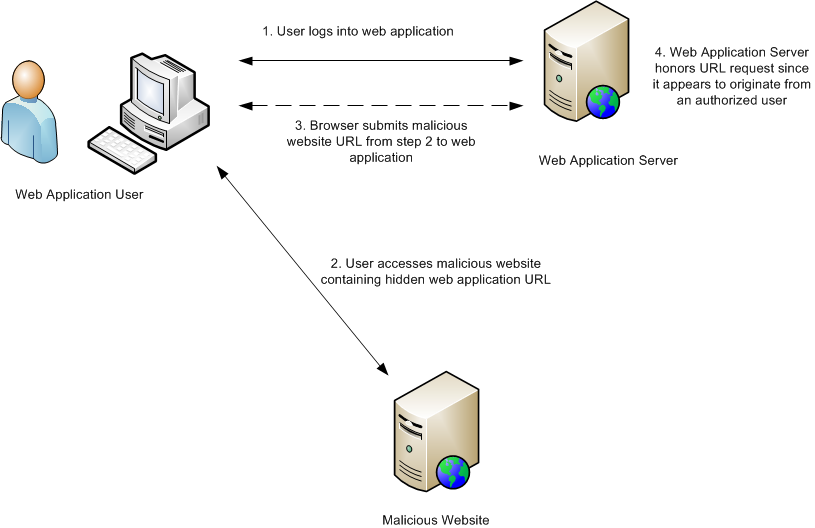
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is an attack that instructs the browser of a victim to send a forged HTTP request to execute actions on a vulnerable web application in which the victim is currently authenticated.
The forged HTTP request can be embedded in emails, chats, or other websites. If the victim visits a forged HTTP request while authenticated to the vulnerable web application, and the victim has permission to perform the action, the attack with succeed.
A successful CSRF exploit can compromise user data, operations, or the entire web application. There is no limit to the impact of a CSRF attack. Some example impacts on PTC FlexPLM are:
• A user could be added to a team for a project, product, or library, allowing them to have access to sensitive data.
• An important document could be deleted.
• Security privileges for an object could be modified, granting additional privileges to unprivileged users, or denying privileges to others.