Configure ThingWorx as a Resource Provider
Configure the resourceServerSettings.json File
This procedure is required when ThingWorx is the Resource Server application.
1. Stop the ThingWorx server.
2. Create the resourceServerSettings.json file in the same directory as sso-settings.json.
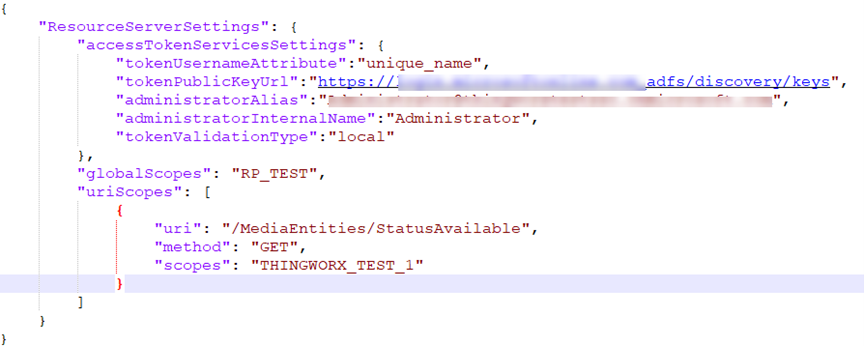
The following is a sample structure of the resourceServerSettings.json file:
{
"ResourceServerSettings": {
"accessTokenServicesSettings": {
"tokenUsernameAttribute": "See information in the table below",
"tokenPublicKeyUrl": "See information in the table below",
"administratorAlias": "See information in the table below",
"administratorInternalName": "Administrator",
"issuer": "See information in the table below",
"tokenValidationType": "local",
"tokenClientIDAttribute": "See information in the table below"
},
"globalScopes": "See information in the table below",
"uriScopes": [
{
"uri": "See information in the table below",
"scopes": "See information in the table below",
"method": "See information in the table below"
}
]
}
"ResourceServerSettings": {
"accessTokenServicesSettings": {
"tokenUsernameAttribute": "See information in the table below",
"tokenPublicKeyUrl": "See information in the table below",
"administratorAlias": "See information in the table below",
"administratorInternalName": "Administrator",
"issuer": "See information in the table below",
"tokenValidationType": "local",
"tokenClientIDAttribute": "See information in the table below"
},
"globalScopes": "See information in the table below",
"uriScopes": [
{
"uri": "See information in the table below",
"scopes": "See information in the table below",
"method": "See information in the table below"
}
]
}
3. Ensure that you edit the value of every parameter as per your requirement. Your implementation may vary depends on several factors, such as the security policies of your organization and the CAS for your federation. Use the information in the following tables as guidance to set values for different parameters.
4. Start the ThingWorx server.
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
Value
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tokenUsernameAttribute
|
Optional: The claim name that holds the username for the resource request.
|
Default value: “unique_name”
|
||
|
tokenPublicKeyUrl
|
Mandatory: The AD FS public key endpoint (used to validate the access tokens).
|
The value is constructed as follows:
https://<ADFS host FQDN>adfs/discovery/keys
|
||
|
administratorAlias
|
Optional.
Mandatory only if you want to access RP with ThingWorx administrator.
|
The administrator username as it is configured in AD FS.
|
||
|
administratorInternalName
|
Optional: The administrator username as it is configured in ThingWorx.
|
Administrator
|
||
|
tokenValidationType
|
Mandatory: The property point that the access token (JWT) validation done locally.
|
local
|
||
|
issuer
|
Optional: Issuer value for additional token validation check.
|
The issuer value as it appears in the ISS claim in the token.
|
||
|
tokenClientIDAttribute
|
Required for the M2M (Client Credential) flow. The claim name that holds the SP clientID for the resource request.
|
appid
|
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|
|
globalScopes
|
List of comma-separated global scopes. accessToken should contain at least one of them to access any resource. If the parameter is missing or empty, THINGWORX is a default global scope.
|
"globalScopes": "THINGWORX
"globalScopes": "THINGWORX_APP1,THINGWORX_APP2" |
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
Value
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
uri
|
URI pattern. Defines the resource or resource group that requires additional scope(s) to the global scope(s).
|
Thingworx/Things/** - control all Things
Thingworx/Things/Thing1 – control Thing1
|
||
|
scopes
|
Comma-delimited list of additional scopes. Only the user that has grants to all listed scopes (including global) is allowed to get resource.
|
|||
|
method
|
Optional. Defines the URI method that the scope will be applied to.
|
Possible values are any methods allowed in REST protocol, such as GET or POST.
|
If there are scopes defined for an URI, then the global scopes plus the defined URI scopes must be granted to access that resource. If there is more than one URI rule applicable for the requested resource, then all relevant scopes must be granted to access that resource. To avoid access to restricted resources, add URIscope to these REST end points with a scope that does not exist in the Authorization server. In addition to scope protection, ThingWorx has its own user-based permissions that will also be applied on top of the scopes. For example, in a case where User A requests a resource with the correct scopes but does not have permission, the request fails with a 403 error.
Example File