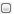
Interface mapping for Java (Java code)
For each Interface, ACS generates an interface in a file of the same name.
The generation of an Interface is derived from the items it owns, properties of the Interface, and the tagged values set for Tag Definitions applied by the «Java Class» stereotype.
• If the Interface owns Classes, ACS typically generates the nested Classes as inner classes.
• If the Interface owns Data Types, ACS typically generates the nested Data Types as inner classes.
If for a nested Data Type the tagged value of the Java Non Member tag definition is set for TRUE, ACS generates the class construct outside of the class construct created for the parent Interface |
• If the Interface owns Dependencies, ACS generates import or implements statements in the code. For Dependency mapping information, click here
Dependency mapping for Java (Java code)
• If the Interface owns Generalizations that define inheritance, ACS generates the Generalizations as extends or implements statements. For Generalization mapping information, click here
Generalization mapping for Java (Java code)
• If the Interface owns Interfaces, ACS typically generates the nested Interfaces as inner interfaces.
If for a nested Interface the tagged value of the Java Non Member tag definition is set for TRUE, ACS generates the interface construct outside of the interface construct created for the parent Interface. |
• If the Interface owns Operations, ACS generates the Operations as methods in the code. For Operation mapping information, click here
Operation mapping for Java (Java code)
• If the Interface owns Roles, ACS generates the Roles as attributes within the code. For Role mapping information, click here
Association and role mapping for Java (Java code)
Other child items are ignored.
• If the Description property has a value, ACS generates the Description as a comment on the line before the interface declaration.
The Description property is also generated as a file comment if the «Java Class» stereotype is not applied to the Interface
• The Formal Template Parameters are generated as the parameters of an Interface set up as a Java Generic through its Template property.
• The Name property is generated as the name of the Java file and as the name of the Java interface in that file.
ACS may modify the interface name that is added to the code to make it valid for Java. You can specify the exact interface name to add to the code through the CODE_GENERATION_NAME property of an Interface.
Tell me more... |
• The Persistent property is ignored.
• The Structure property is ignored.
• If the Template property is set.
• If the Template property is set to TRUE (Template check box selected on Property Pages), the Interface is generated as a Java generic.
• The Template Specialization property (and any Template Specialization Parameters) is ignored.
• The Union property is ignored.
• The Visibility property is generated as follows:
◦ For non-nested Interfaces, ACS ignores the Visibility. Non-nested Interfaces are generated as Public, unless the tagged value of the Java Default Access tag definition is set to TRUE.
◦ For nested Interfaces, the Interface is generated as either Public, Private or Protected, unless the tagged value of the Java Default Access tag definition is set to TRUE. If the tagged value of the Java Default Access tag definition is set to TRUE, the Visibility property is ignored.
If the «Java Module» stereotype is applied to the Interface, ACS generates a Java file for the Interface, but the Interface is not defined as a Java interface in that file.
The following Tag Definitions are applied to a Interface by the «Java Class» stereotype:
• If the tagged value of the Java Default Access tag definition is set to TRUE, ACS generates the Java interface with no access specifier.
• If the tagged value of the Java Extends Text tag definition has been set, the value is generated as the extends statements for the Java interface.
Reverser Notes: When reverse engineering extends statements, the Reverser attempts to model the extends statements as Generalizations in the Model. If the Reverser cannot model the extends statements through Generalizations, the extends statements are recorded through the Java Extends Text tag definition. |
• If the tagged value of the Java File tag definition has been set, the value is used when opening an associated Java file from Modeler. This value is set by ACS.
• If the tagged value of the Java File Comment tag definition has been set, ACS generates the value at the top of the Java file.
• If the tagged value of the Java Final tag definition is set to TRUE, ACS generates the Java interface as final.
• The Java Is Static tag definition does not apply to an Interface.
• If for a nested Interface the tagged value of the Java Non Member tag definition is set to TRUE, ACS generates the interface construct outside of the class or interface construct created for the parent item (interface constructs for nested Interfaces are generated in the Java file created for the parent item).
• The Java Implements Text tag definition does not apply to an Interface.
• If the tagged value of the Java Import Text tag definition has been set, the value is generated as import statements for the Java interface.