NSV-4 Functionality hierarchy (UPDM - NAF aliases)

Creation
To create an NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy:
• Right-click the
Architectural Description or
Service Description that is to own the NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy, point to New, point to Diagram, point to NAF, and then click NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy.
Purpose
On an NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy:
• Create
Capability,
Capability Configuration,
Function,
Organization,
Physical Architecture,
Post,
Resource Artifact,
Responsibility,
Service Access and
Software elements.
• Create
Resource Constraint and
Service Policy elements and apply them to valid elements on the diagram.
Diagram Elements
For information about showing compartments on diagram symbols, setting up default view options and adding existing elements to the diagram, click here

To create an Architectural Description: click the  Architectural Description button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Architectural Description button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Architectural Description button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Architectural Description button, and then click in free space on the diagram.To populate elements from an Architectural Description: add the Architectural Description to the diagram, and then populate those elements from the Architectural Description.

To create an Architectural Reference: click the  Architectural Reference button, click the source Architectural Description, and then click the destination Architectural Description.
Architectural Reference button, click the source Architectural Description, and then click the destination Architectural Description.
 Architectural Reference button, click the source Architectural Description, and then click the destination Architectural Description.
Architectural Reference button, click the source Architectural Description, and then click the destination Architectural Description.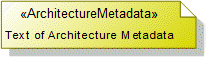
To create an Architecture Metadata: click the  Architecture Metadata button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Architecture Metadata button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Architecture Metadata button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Architecture Metadata button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Define the text of the Architecture Metadata through its Full Text property.
To apply an Architecture Metadata to an Architectural Description: click the  Note Link button, click the Architecture Metadata, and then click the Architectural Description to which the Architecture Metadata applies.
Note Link button, click the Architecture Metadata, and then click the Architectural Description to which the Architecture Metadata applies.
 Note Link button, click the Architecture Metadata, and then click the Architectural Description to which the Architecture Metadata applies.
Note Link button, click the Architecture Metadata, and then click the Architectural Description to which the Architecture Metadata applies.
To create a Capability: click the  Capability button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Capability button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Capability button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Capability button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Maps To Capability relationships to link the Capability to Function elements that map to that Capability.

To create a Capability Configuration: click the  Capability Configuration button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Capability Configuration button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Capability Configuration button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Capability Configuration button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Capability Configuration to the Function elements that the Capability Configuration can perform.

To create a Function: click the  Function button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Function button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Function button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Function button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Function to elements that can perform that Function. The following elements can perform a Function: Capability Configuration, Organization, Physical Architecture, Post, Responsibility, Service Access and Software elements.

To create a Function Action: click the  Function Action button, click the calling Function, and then click the invoked Function.
Function Action button, click the calling Function, and then click the invoked Function.
 Function Action button, click the calling Function, and then click the invoked Function.
Function Action button, click the calling Function, and then click the invoked Function.
To create an Is Capable Of Performing: click the  Is Capable Of Performing button, click the source element, and then click the Function that can be performed.
Is Capable Of Performing button, click the source element, and then click the Function that can be performed.
 Is Capable Of Performing button, click the source element, and then click the Function that can be performed.
Is Capable Of Performing button, click the source element, and then click the Function that can be performed.The source element can be a Capability Configuration, Organization, Physical Architecture, Post, Responsibility, Service Access or Software element.

To create a Maps To Capability: click the  Maps To Capability button, click the Function, and then click the Capability that is mapped to.
Maps To Capability button, click the Function, and then click the Capability that is mapped to.
 Maps To Capability button, click the Function, and then click the Capability that is mapped to.
Maps To Capability button, click the Function, and then click the Capability that is mapped to.
To create an Organization: click the  Organization button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Organization button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Organization button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Organization button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Organization to the Function elements that the Organization can perform.

To create a Physical Architecture: click the  Physical Architecture button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Physical Architecture button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Physical Architecture button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Physical Architecture button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Physical Architecture to the Function elements that the Physical Architecture can perform.

To create a Post: click the  Post button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Post button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Post button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Post button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Post to the Function elements that the Post can perform.

To create a Resource Artifact: click the  Resource Artifact button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Resource Artifact button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Resource Artifact button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Resource Artifact button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Resource Artifact to the Function elements that the Resource Artifact can perform.

To create a Resource Constraint: click the  Resource Constraint button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Resource Constraint.
Resource Constraint button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Resource Constraint.
 Resource Constraint button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Resource Constraint.
Resource Constraint button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Resource Constraint.To apply a Resource Constraint to an element on the diagram: click the  Note Link button, click the Resource Constraint, and then click the element to which the Resource Constraint applies.
Note Link button, click the Resource Constraint, and then click the element to which the Resource Constraint applies.
 Note Link button, click the Resource Constraint, and then click the element to which the Resource Constraint applies.
Note Link button, click the Resource Constraint, and then click the element to which the Resource Constraint applies.You can apply a Resource Constraint to Capability Configuration, Function, Organization, Physical Architecture, Post, Responsibility, Service Access and Software elements.

To create a Responsibility: click the  Responsibility button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Responsibility button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Responsibility button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Responsibility button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Responsibility to the Function elements that the Responsibility can perform.

To create a Service Access: click the  Service Access button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Service Access button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Service Access button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Service Access button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Service Access to the Function elements that the Service Access can perform.

To create a Service Policy: click the  Service Policy button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Service Policy.
Service Policy button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Service Policy.
 Service Policy button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Service Policy.
Service Policy button, and then click in free space on the diagram. Use the Full Text property to specify the text of the Service Policy.To apply a Service Policy to an element on the diagram: click the  Note Link button, click the Service Policy, and then click the element to which the Service Policy applies.
Note Link button, click the Service Policy, and then click the element to which the Service Policy applies.
 Note Link button, click the Service Policy, and then click the element to which the Service Policy applies.
Note Link button, click the Service Policy, and then click the element to which the Service Policy applies.You can apply a Service Policy to Capability Configuration, Organization, Physical Architecture, Post, Responsibility, Service Access and Software elements.

To create a Software: click the  Software button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Software button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
 Software button, and then click in free space on the diagram.
Software button, and then click in free space on the diagram.Use Is Capable Of Performing relationships to link the Software to the Function elements that the Software can perform.
The following sections provide information about how an NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy is used in the model.
Create an NSV-4 Functionality Hierarchy from
Creates or shows these UPDM elements
In addition to the common UPDM elements that can be shown on all Product diagrams (
Alias,
Definition,
Information,
Metadata,
Overlap and
Same As elements):