Example: Wiener Filtering
Use the wiener2d function to reduce additive random noise in images.
Wiener filtering was one of the first methods developed to reduce additive random noise in images. It works on the assumption that additive noise is a stationary random process, independent of pixel location; the algorithm minimizes the square error between the original and reconstructed images.
For information on using this example, refer to About Image Processing Examples.
Using Random Uniform Distribution Noise
1. Create a simple rectangular box image
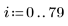
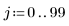
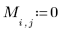
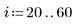
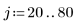
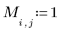
2. Use the runif function to add noise to the box image.
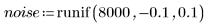
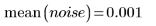
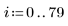
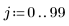
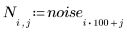
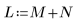
3. Use a 7 x 7 window Wiener filter on the image.
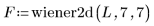
4. Use the scale function to scale and display the two images:
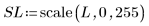
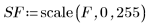
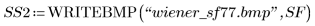
 |  |
(wiener_sl.bmp) | (wiener_sf77.bmp) |
The outlines of the square have not been blurred, but the noise has been smoothed. However, the noise is not filtered out near the square outlines for a neighborhood the size of the filtering window.
5. Use a 3 x 3 window on the image.
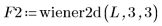
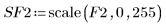
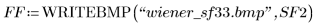
 | |
(wiener_sf33.bmp) |
In this image, there is less overall smoothing, but it extends nearer to the square outlines.
Using Gaussian Noise
1. Read in an image file and degrade it by random white Gaussian noise.
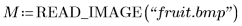
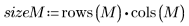
2. Use the rnorm function to add Gaussian noise to the image.
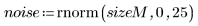
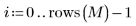
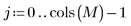
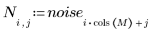
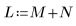
3. Use the scale function to scale the two images.
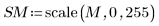
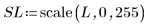
 |  |
(fruit_sm.bmp) | (fruit_sl.bmp) |
4. Suppress the noise using Wiener filtering with a 5 x 5 window.
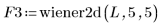
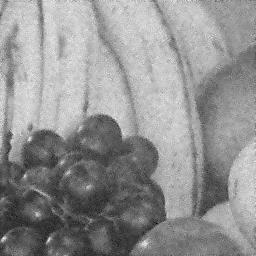 | |
(fruit_w55.bmp) |