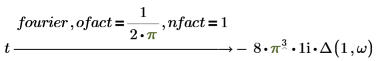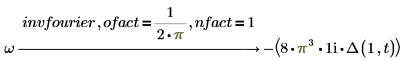Example: Using nfact and ofact modifiers
The normalization multipliers (nfact) and oscillatory factor (ofact) are expressed as follows:
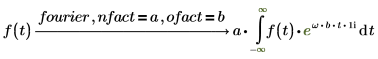
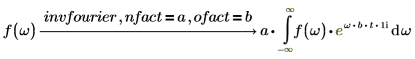
Fourier and inverse Fourier transformations only differ with normalization and oscillatory factors. The factors are usually chosen such that subsequent performance of direct and inverse transformation gives the original function. For example:
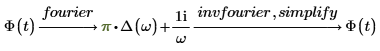
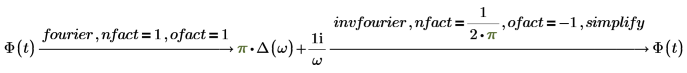
In different fields of mathematics and engineering the pairs of normalization and oscillatory factors are chosen differently to normalize different types of signals.
1. Probability theory (models with no units)
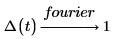
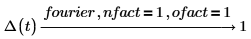
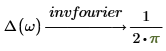
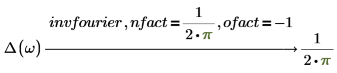
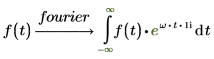
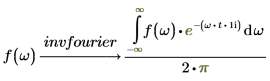
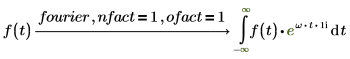
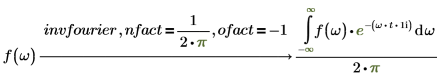
2. Electric engineering (frequency in hertz, one of the Wolfram sets)
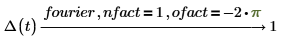
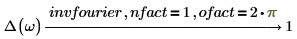
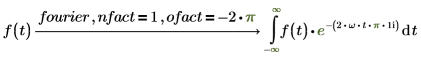
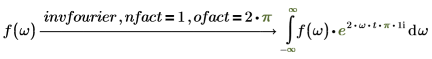
3. Electric engineering (angular frequency is used)
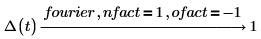
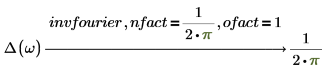
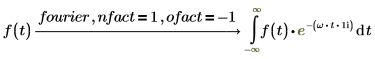
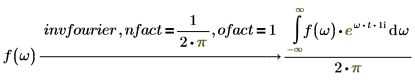
4. In symmetry of direct and inverse, transformation is important. The same input (with different variable of transformation) returns the same output result by using appropriate set of nfact and ofact values.
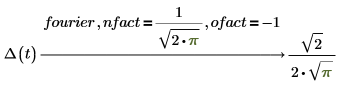
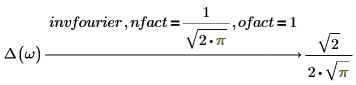
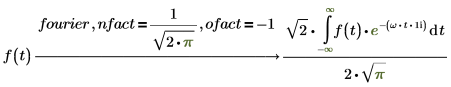
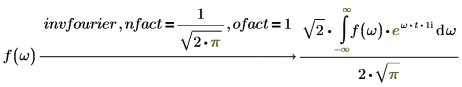
Invertibility between Fourier and inverse Fourier
When applying the keyword fourier on an input expression, then applying of keyword invfourier on the result must return to initial expression. The invertibility is supported when using keywords fourier or invfourier with default nfact and ofact modifiers.
The following conditions apply while using the nfact and ofact modifiers:
• Include the nfact and ofact modifiers immediately after the keyword name. You can use the two modifiers separately or include both in an expression.
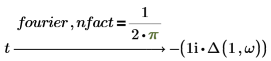
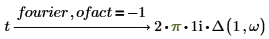
• Matrices are not allowed as factors.
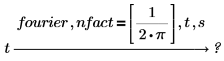
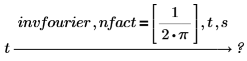
• The inverse order of modifiers is acceptable.