Built-In Constants and Variables
Math Constants
|
Constant
|
Keystroke
|
Name
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
∞
|
Ctrl+Shift+Z
|
Infinity
|
 |
|
e
|
e
|
Logarithm base
|
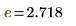 |
|
π
|
p, Ctrl+G
|
Pi
|
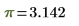 |
Other Constants
|
Constant
|
Keystroke
|
Name
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
i or j
|
1i or 1j
|
The imaginary units
|
Square root of –1
|
|
NaN
|
NaN
|
Not a Number
|
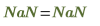 |
Physics Constants
|
Constant
|
Keystroke
|
Name
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
c
|
Speed of light in vacuum
|
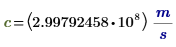 |
|
|
ec
|
Elementary charge
|
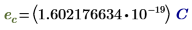 |
|
|
h
|
Planck's constant
|
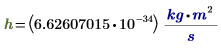 |
|
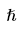 |
Reduced Planck's constant (h/2π)
|
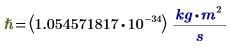 |
|
|
k
|
Boltzmann constant
|
 |
|
|
mu
|
Atomic mass unit
|
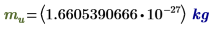 |
|
|
NA
|
Avogadro's number
|
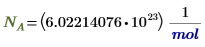 |
|
|
R
|
Molar gas constant
|
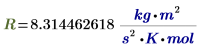 |
|
|
R∞
|
Rydberg constant
|
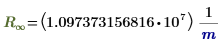 |
|
|
α
|
a, Ctrl+G
|
Fine structure constant
|
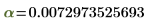 |
|
γ
|
g, Ctrl+G
|
Euler-Mascheroni's constant
|
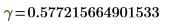 |
|
ε0
|
Permittivity of free space
|
 |
|
|
μ0
|
Magnetic permeability of free space
|
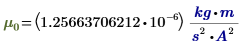 |
|
|
σ
|
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
|
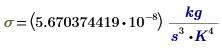 |
|
|
Φ0
|
Magnetic flux quantum
|
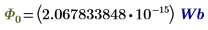 |
System Variables
|
Name
|
Default Value
|
Use
|
|---|---|---|
|
TOL
|
0.001
|
|
|
CTOL
|
0.001
|
|
|
ORIGIN
|
0
|
Controls array indexing. You can reset ORIGIN to 1 on the Calculation tab, or you can redefine ORIGIN to another value in your worksheet.
|
|
PRNPRECISION
|
4
|
|
|
PRNCOLWIDTH
|
8
|
Controls the width of columns in an ASCII data file created by the WRITEPRN or APPENDPRN functions.
|
|
CWD
|
Current working directory
(in the form of a string variable)
|
Use this system variable as an argument to file handling functions.
|
|
CustomFunctions
|
When custom functions exist, each row holds information about a single custom function, where:
• First column—A string containing the filename of the DLL that contains the definition of the custom function.
• Second column—A string containing the name of the custom function.
• Third column—The custom function object. This value can be assigned to a variable to be used as the new function name, such as:
my_cust_func:=CustomFunctions0,2
|