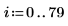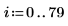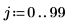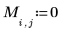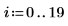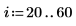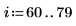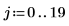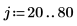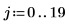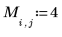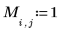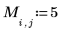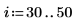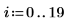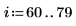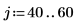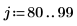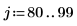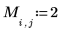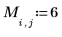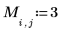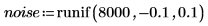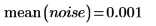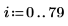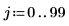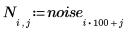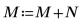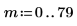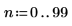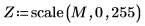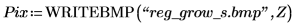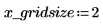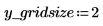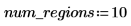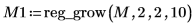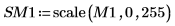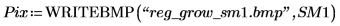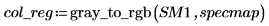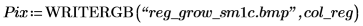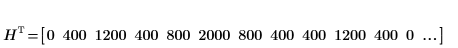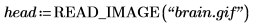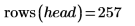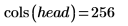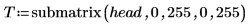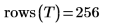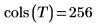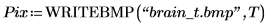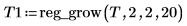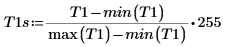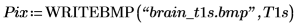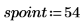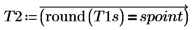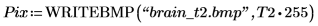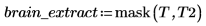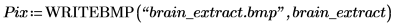Example: Region Growing
The reg_grow function divides an image into several homogenous connected regions using a region-growing algorithm. Region-based segmentation is used to group regions in an image that bear homogeneous properties, such as intensity, texture, and so on.
For information on using this example, refer to
About Image Processing Examples .
1.
2.
3.
(reg_grow_s.bmp)
4.
5.
(reg_grow_sm1.bmp)
6.
(reg_grow_sm1c.bmp)
7.
As in the input matrix, there are five regions with area of 400, two regions of 800, and three regions of 2000.
8.
9.
10.
11.
(brain_t.bmp)
(brain_t1s.bmp)
12. spoint .
T2 is a binary image:
(brain_t2.bmp)
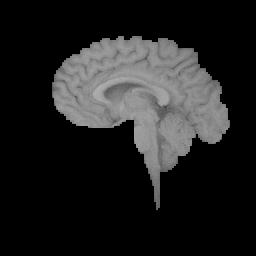
13. T2 as a mask to extract the brain region out of the original image.
(brain_extract.bmp)
Copy Expressions