![Integration Kit What's New [Integration Kit What's New]](../Nav02_WhatsNew.png)
![Integration Kit What's New [Integration Kit What's New]](../Nav02_WhatsNew.png) |
See also: Dialog Generator Manual
A copilot consists of handles and feedback in the graphics area that make it simple and staightforward to specify geometrical intent. The copilot enables intuitive direct manipulations on objects and reduces the need to interact via UI controls in a separate window.
A copilot consists of the following 3 components
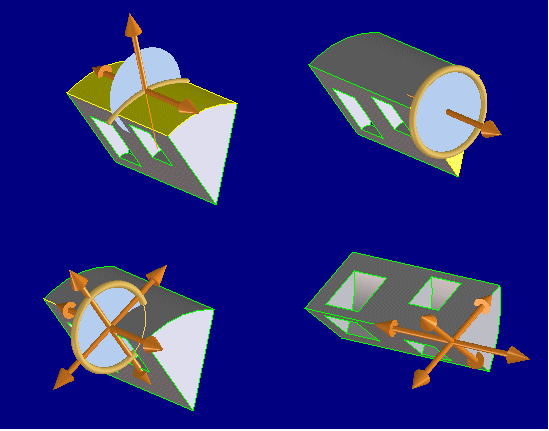
The images below illustrate a polestar, containing the major types of components, and a circular polestar.
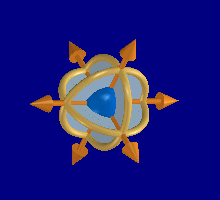

When a user selects a polestar component, a predefinable pick token and a pick point are issued to the input buffer. These inputs are received by the currently active dialog.
The pick token typically activates a dialog variable. That dialog
variable then receives the pick point which then initiates the dragger.
The geometrical properties of the selected polestar can be inquired and
exploited in the code attachments of the activated variable, e.g. in
:before-input. On completion of the drag, the
:after-input code of the entered variable is excecuted.
A pick on a polestar component contains much more information than is available by using simple UI controls such a buttons, checkboxes, ranges and input fields.
A set of functions are provided to create, inquire and destroy a polestar.
The state of the drag motion is displayed by appropriate drag feedback. The images below illustrate linear, planar and circular drag feedback:
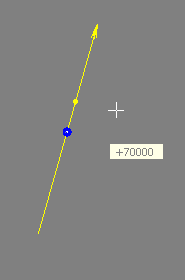
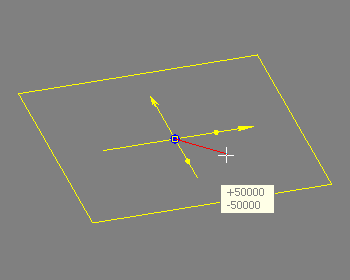
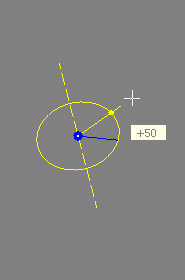
The blue point marks the initial drag position while the yellow point represents the current drag value. The current drag position is displayed numerically in a cursor text window that moves in sync with the mouse cursor.
It is possible to attach the polestar and a quickview to the constrained drag motion.
The dragger can be specified by adding drag options to a dialog variable. Such a variable is called a drag variable.
The dragger feedback is activated as soon as the drag variable is entered and a pick point is received. Thus, for example, a pick on a polestar component can activate a drag variable which then immediately generates drag feedback in the graphics window.
The image below illustrates a predefined quickview called :extrude-profile.
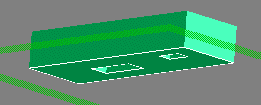
Several other predefined quickviews are supported. Furthermore, arbitrary quickview feedback can be created by means of LISP application code.
A quickview can be obtained by adding quickview options to a drag variable.
The quickview is automatically generated as soon as the drag feedback is created. Further functions are provided to create, inquire and delete quickview feedback.
The polestar or the dragger can be omitted from the copilot, but one of the two must be present.
The following functions can be used to create, inquire, activate, deactivate and delete a polestar.
(sd-create-polestar :pick-token pick-token
:origin origin
:dir dir
:forward-picking boolean
:no-vport-pick boolean
:components components)
Polestars are automatically managed in the following ways:
Warning: In order to obtain the above built-in polestar
management, the polestar must be created in sync with the dialog, e.g.
in forms like :before-input and :after-input
or in functions called from these forms. Polestars used within a dialog
should not be created outside the scope of the dialog, e.g. in a
subaction called by the dialog. In particular, polestars should not be
created in a :feedback-update-function,
since this option is executed while the drag subaction is active.
Furthermore, polestars should not be generated in UI-related forms, such
as :after-input-ui.
:pick-token specification.:origin specification (see below).:dir, has a :dir specification.T, the
polestar pick data will contain a direction towards the pick point
rather than the direction in the polestar.
This argument is optional.
This option is useful when picking on one of the linear arrows of a classic polestar, resulting in directions that point out from the polestar center. (see Co_View dialog).
The default NIL generates the same polestar pick
direction that was supplied when the polestar was created.
:pick-token is sent to the input buffer.
((:type :line
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:origin 3d-vector ; default=default origin
:dir 3d-vector ; default=default dir
:forward-arrow boolean ; default=t
:backward-arrow boolean ; default=t
:mid-disc boolean ; default=nil
:forward-only boolean ; default=nil
:label string ; default=nil
)
(:type :arc
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:origin 3d-vector ; default=default origin
:dir 3d-vector ; default=default dir
:mid-help-pos 3d-vector
;The vector :mid-help-pos H is projected onto the
;axis giving point C, the center of the arc.
;The direction H-C is used as the direction
;towards the middle of the arc (where the disc
;is drawn). The actual position of this disc
;depends on the viewport scale.
:forward-arrow boolean ; default=t
:backward-arrow boolean ; default=t
:mid-disc boolean ; default=nil
)
(:type :disc
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:origin 3d-vector ; default=default origin
:dir 3d-vector ; default=default dir
)
(:type :ring
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:origin 3d-vector ; default=default origin
:dir 3d-vector ; default=default dir
)
(:type :model-ring ;This component is intended to be generated
;only via the function sd-classic-polestar-components
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:center 3d-vector
:dir 3d-vector
:mid-dir 3d-vector ; direction from the ring/arc center
; towards the pick point.
; When a model ring is not a full circle
; (this depends on the view scale at
; creation time) the mid point of the arc
; is generally placed at the picked point.
; However, because the radius can vary
; supplying the mid point is more general.
:radius number
)
(:type :sphere
:pick-token string ; default=default pick-token
:origin 3d-vector ; default=default origin
)
)
Each component can overwrite the default :pick-token,
:origin and :dir values - whenever
applicable.
However, there is a restriction
for the :origin specifications: all component origins
must be equal. If a default origin is specified, then the individual
component origins are ignored and replaced by the default origin. If
no default origin is specified, then all component origins must be
equal. If not, the first specified component origin is used for all
the other components.
When a user clicks on a polestar component, usually two inputs are sent to the input buffer:
:pick-token associated with the picked
component, followed byIf the option :no-vport-pick is set, no pick point
is generated.
The :pick-token can be used to activate a dialog
variable. That dialog variable then receives the pick point. The
receiving variable must be designed to receive a pick point and
should be either
:point-3d-pick.Note: If the :pick-token string starts with a left
parenthesis (, the string will be evaluated before the
evaluation result (has to be a string or a keyword) is sent to the
input buffer. That way you can execute some LISP expression which
determines the pick-token at runtime.
The details of the picked polestar component can be inquired within the dialog by means of the function sd-inq-polestar-pick
(sd-create-polestar
:components
(list (list :type :line
:dir 1,0,0
:origin 0,0,0
:pick-token ":DISTANCE" )
(list :type :line
:dir 0,1,0
:origin 0,0,0
:pick-token ":DISTANCE")))
where a dialog variable called DISTANCE is assumed to
exist.
(sd-delete-polestar polestar)
Note: If a polestar is not explicitly deleted by means of this call, then it will automatically be deleted when the dialog terminates.
(sd-delete-polestar polestar)
(sd-classic-polestar-components sel_item position)
(sd-classic-polestar-components (first ref) (second ref))where ref assumed to be a dialog variable with a selection and a
:incl-position :3d option.
See also example 6.1. View Copilot
(sd-inq-polestar-pick polestar property)
The returned values depend on the type of the polestar component that was picked:
The value of :zero-pos is used to position the dragger
at an initial non-zero value that corresponds to the initial pick
position. This behavior occurs when the :jump option
is set to T (which is the default, unless
:polestar-passenger is set to T). If
:jump is set to NIL, then the dragger starts
smoothly without the initial 'jump'.
(sd-activate-polestar polestar)
Note: A polestar is automatically deactivated and reactivated while it triggers a drag variable or when an interrupt dialog suspends the current dialog.
(sd-activate-polestar polestar)
(sd-deactivate-polestar polestar &optional freeze-colors)
Note: A polestar is automatically deactivated and reactivated while it triggers a drag variable or when an interrupt dialog suspends the current dialog.
(sd-deactivate-polestar polestar)
(sd-inq-profile-center workplane)
This function is used to determine the position of a circular
polestar in the turn command.
(sd-inq-profile-center wp)
(sd-get-visible-profile-pnt workplane)
This function is used to determine the position of a linear polestar
in the extrude command.
(sd-get-visible-profile-pnt wp)
(sd-get-picked-polestar)
(sd-get-picked-polestar)
A dialog variable that contains drag is called a drag variable, as mentioned in the introduction. This section describes the available drag and quickview options. Additional functions are provided to further control and inquire quickviews.
A drag variable generates the drag feedback as soon as the variable is
activated and has received a pick point. The variable is typically activated
via the input buffer, for example by specifying the variable name in the
:pick-token of a polestar.
A drag variable can contain many of the variable options that are
applicable to any dialog variable, provided they are compatible with the
copilot usage. For example, if a variable contains
:before-input, :after-input,
:start-input-feedback and :end-input-feedback
forms, the following sequence of actions is carried out when the drag
variable is activated and has received a pick point:
:before-input is executed,:start-input-feedback is executed,:end-input-feedback is executed, when the drag terminated
positively or negatively,:after-input is executed, provided the drag terminated
positively.A drag variable can have the value type :length or
:angle. In this case, an input to that variable can be entered
in two ways: either by the usual explicit data entry (into the variable's
input field or into the user input line) and by means of dragging.
If the drag variable has the value type :length or
:angle and is visible, then the value of the current drag
distance or angle is displayed in the variable's text field during the drag
motion.
(sd-defdialog 'dialog-name
:variables
'(...
(VARIABLE_X
:drag-from-polestar a-polestar or :picked-polestar
;
; Used as source of default values for several
; of the drag options listed below.
;
; Deactivates the specified polestar while dragging.
;
; If several polestars can trigger the same
; drag variable, then the value :picked-polestar
; selects the picked polestar as basis for the
; dragging. The selected polestar can be
; accessed via the call sd-get-picked-polestar.
;
:drag-mode :linear ; Drag along the specified line
:circular ; Drag around the specified axis
:planar ; Drag within the specified plane
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar:
; - :linear if a :line component was selected
; - :circular if a :ring or :circular component was selected
; - :planar if a :disc component was selected
;; Options for a Linear Drag Mode:
:drag-line-dir 3d-vector
; Line direction for a linear drag mode.
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar.
:drag-max-value number
; Upper limit for a linear drag.
; The default is nil, that is, no limit is imposed.
:drag-min-value number
; Lower limit for a linear drag.
; The default is nil, that is, no limit is imposed.
:drag-scale number
; Scale for a linear drag.
; The default is 1.
:offset number
; Offset for a linear drag.
; The default is zero.
;; Options for a Circular Drag Mode:
:drag-circle-cen 3d-vector
; Circle center for a circular drag.
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar.
:drag-circle-axis 3d-vector
; Circle axis for a circular drag.
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar.
:drag-plus-minus-range {t nil}
; default=t
; By default angles are displayed between -180 and +180 degrees.
; If this option is set to nil, then angles are no longer
; limited to this range.
;; Options for a Planar Drag Mode:
:drag-plane-nor 3d-vector
; Plane normal for a planar drag.
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar.
;; Options for all Drag Modes:
:drag-zero-pos 3d-vector
; Zero position for drag motion.
; The default is derived from :drag-from-polestar.
:result-type :distance ; Assign drag distance to drag variable.
:angle ; Assign drag angle to drag variable.
:vector-transform ; Assign drag vector transform to drag variable.
; The default is basically derived from the :value-type
; of the drag variable:
; - :distance if :value-type = :length
; - :angle if :value-type = :angle
; - :vector-transform if :value-type <> :length or :angle
or
if :quickview-type = :lisp-feedback
:polestar-passenger {t nil}
; default=nil
; Causes the polestar specified in :drag-from-polestar
; to move together with the drag motion.
:jump {t nil}
; default=nil if :polestar-passenger=t
; t otherwise
; If this option is T, the dragger jumps to
; an initial non-zero position corresponding to
; the picked position. In this case drag start
; position differs from the drag zero position.
;
; If this option is NIL, the drag starts smoothly
; from the zero position.
;
; The zero position is in most cases the polestar
; origin. One exception is the ring, where the
; mid pos (the position of the mid disc) is used
; as the zero point (see also sd-inq-polestar-pick.)
:initial-prompt-text string
; default="Drag or enter value."
; This initial prompt text is displayed
; when entering the dragger and waiting for a
; pick point to be entered.
:eat-pick {t nil}
; default=t
; A pick on a polestar component issues a :pick-token
; and a pick point. By default, the pick point itself
; is not processed by the drag variable, but is
; rathermore 'eaten'. All relevant drag data is
; by default inquired from the picked polestar.
; In applications not involving a polestar, the
; option :eat-pick nil allows the dragger to be
; activated without needing to have a pick point.
:fast-complete {t nil}
; default=t
; Causes a middle-mouse click during up mouse
; dragging to immediately complete the dragging
; positively.
; If this option is set to nil, then a middle
; mouse click during the up mouse drag will
; cancel the drag.
)
)
)
See also: Dialog Generator Manual
There are three ways to specify a dragger:
Note that :pick-token of the specified polestar needs to
correspond to the current drag variable name. A click on the polestar
will activate the variable and will then automatically generate the
following kinds of drags:
The explicitly specified drag options overwrite the drag options that are internally derived from the polestar.
A quickview is created if the :quickview-type option and the
corresponding additional options are specified.
The quickview is created immediately when the drag variable is entered or, alternatively, when the function sd-create-quickview or sd-modify-quickview is called.
The quickview follows the movement of the dragger as soon as the drag feedback has been activated.
In general, the quickview is destroyed either automatically as the dialog
terminates or explicitly when the function sd-delete-quickview is called. A quickview of the type
:qv-parcel or :lisp-feedback is automatically
destroyed after the completion of the drag.
(sd-defdialog 'dialog-name
:variables
'(...
(VARIABLE_X
;-- Profile-based Quickview -- (Example 6.2. Extrude Copilot)
;
; Creates solid quickviews derived from a profile in a workplane.
:quickview-type :extrude-profile ; Extrudes a solid from a profile.
:mill-profile ; Mills a solid from a profile.
:turn-profile ; Turns a solid from a profile.
:bore-profile ; Bores a solid from a profile.
:quickview-wp workplane-sel_item
:quickview-shaded {t nil} ; default=t
:quickview-dir 3d-vector ; default=normal to :quickview-wp
:quickview-use-both-sides {t nil} ; default=nil
;-- Parcel-based Quickview -- (Example 6.3. Parcels Copilot)
;
; Creates solid quickviews derived from parcels, e.g. parts, assemblies,
; workplanes and wpsets.
; This quickview can be used to reposition parcels.
:quickview-type :qv-parcel ; Drags parcels, e.g. parts and workplanes.
; This quickview drags parcels to a new
; position.
:quickview-parcels sel_items ; the dragged parcels are derived from
; these sel_items.
:transfer-to-model {t nil} ; default=t
; By default the model state is changed by the
; quickview, that is, the dragged parcel is
; moved to a new position. If set to nil, this
; option suppresses the modeling behavior of the
; quickview and deletes the quickview after
; the drag.
;-- Lisp-based Quickview -- (Example 6.4. Cable Copilot)
;
; Calls application-oriented lisp feedback functions during the drag.
; A quickview structure that contains the state of the drag is
; passed to the lisp feedback functions (see sd-inq-quickview).
:quickview-type :lisp-feedback
:feedback-init-function function-name ; default=nil
; A function for initializing
; lisp-based feedback.
; The function must accept one argument,
; the quickview.
:feedback-update-function function-name ; A function for updating
; lisp-based feedback during the
; drag.
; The function must accept one argument,
; the quickview.
:feedback-destroy-function function-name ; default=nil
; a function for destroying
; feedback upon completion of the
; drag.
; The function must accept one argument,
; the quickview.
:feedback-apply-function function-name ; default=nil
; a function to be executed
; after the drag.
; The function must accept one argument,
; the quickview.
; The above quickview feedback functions can be local dialog functions,
; that access and modify dialog variables, and can call other dialog
; specific local functions. Dialog variables with text fields that
; are modified in these feedback functions are instantaneously updated
; in the UI during the drag.
; The following restrictions apply:
; 1. The feedback functions are not allowed to call
; built-in local functions, such as sd-set-variable-status.
; This restriction does not apply to the quickview apply
; function.
; 2. Variable options that update UI, like :after-input-ui,
; are ignored during the drag.
:offset number ; default=0
; Specifies an initial offset for
; the drag distance that is displayed
; in the drag text field and in the cursor
; text window.
;-- General Quickview Option
:quickview-precondition {t nil}
; default=t
; Quickviews are internally created, manipulated
; and destroyed when this option is set to t.
; This option can be used to suppress these quickview
; manipulations while some of the quickview are undefined.
)
)
)
See also: Dialog Generator Manual
(sd-inq-quickview quickview property)
(sd-inq-quickview qv :distance)
(sd-modify-quickview variable value)
:result-type and :value-type of the
variable.(sd-modify-quickview :dragged-position 23) (sd-modify-quickview 'dragged-position 23)
(sd-delete-quickview variable)
:qv-parcel which are deleted
immediately after a successful drag action.
(sd-delete-quickview :dragged-position) (sd-delete-quickview 'dragged-position)
(sd-create-quickview variable)
Quickviews are automatically created before the
:before-input code of the quickview variable is reached.
After deleting that quickview, this function can be used to create a new
quickview, using the current values of the quickview options (see
3.3. Quickview Options.
This function has no effect if the quickview already exists. A previously existing quickview can be removed by means of the function sd-delete-quickview.
(sd-create-quickview :dragged-position) (sd-create-quickview 'dragged-position)
(sd-get-quickview variable)
(sd-get-quickview :dragged-position) (sd-get-quickview 'dragged-position)
It is possible to control the recording of the drag motion while creating recorder files.
If the flag Include Motion is switched off (the default),
then the recorder file will contain the final drag position. This will lead
to a fast replay of the recorder file. If the flag Include
Motion is switched on, then the recorder file will contain the entire
drag information. In this mode the original drag motion is reproduced during
the replay of the recorder file.
This example illustrates the use of a polestar. The dialog aligns the current view to a selected face, edge or vertex.
This dialog has no UI window. The user can click on a face, edge or vertex to create a classic polestar as illustrated below.
After the selection of an element, the dialog returns to the prompt state
called REF that allows the user to select another element.
Alternatively, the user can select a polestar component. That component
selection causes the activation of an invisible variable called
POLESTAR_PICK, which sets the current view to be perpendicular
to the direction of the selected component. The dialog then returns to the
prompting state REF, where it waits for the next user
input.
(sd-defdialog 'co_view
:without-show t
:prompt-variable 'ref
:variables
'((POLESTAR)
(REF :selection (*sd-face-seltype*
*sd-edge-3d-seltype*
*sd-vertex-3d-seltype*)
:incl-position :3d
:after-input
(progn
(sd-delete-polestar POLESTAR)
(setq POLESTAR
(sd-create-polestar
:pick-token ":polestar_pick"
:forward-picking t
:components (sd-classic-polestar-components
(first ref) (second ref))
)
)
)
)
(POLESTAR_PICK
:value-type :point-3d-pick
:after-input
(set-copilot-view
(second ref)
(sd-inq-polestar-pick polestar :dir))
)
)
)
(defun set-copilot-view (pos dir)
(let ((vp-name (sd-inq-current-vp)))
(when pos
(set_vp_to_point vp-name pos)
;avoid sd-call-cmds in above interrupt action
;to obtain interpolated camera update.
)
(when dir
(sd-call-cmds
(set_vp_direction vp-name (sd-vec-subtract 0,0,0 dir))))
)
)
This example illustrates a polestar that triggers a linear drag and a predefined quickview feedback.
The dialog extrudes a profile by dragging. Alternatively, the extrude distance can be entered numerically into the distance input field. Note that the distance can be entered even before the workplane has been specified, that is before the polestar and quickview exist.
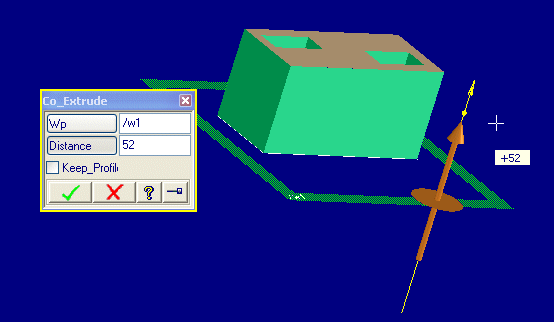
(sd-defdialog 'co_extrude
:variables
'((POLESTAR)
(WP :value-type :wp-with-profile
:incl-position :3d
:after-input
(progn
(sd-delete-polestar polestar)
(setq POLESTAR
(sd-create-polestar
:components
(list (list :type :line
:pick-token ":DISTANCE"
:origin (second WP)
:dir (sd-inq-wp-w-dir (first WP))
:backward-arrow nil
:mid-disc t))))
(sd-modify-quickview 'distance distance))
)
(DISTANCE
:value-type :length
:drag-from-polestar POLESTAR
:quickview-type :extrude-profile
:quickview-wp WP
)
(KEEP_PROFILE :value-type :boolean)
)
:ok-action
'(sd-call-cmds
(extrude
:wp (first wp)
:auto_direction :yes
:keep_wp :yes
:keep_profile (if keep_profile :yes :no)
:direction :+w
:distance distance
)
)
)
This example illustrates a parcel-based drag derived from a classic polestar.
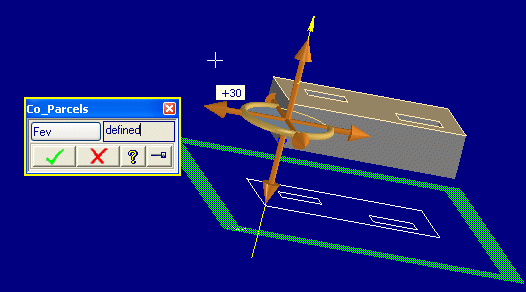
(sd-defdialog 'co_parcels
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
:variables
`((POLESTAR)
(FEV
:selection (*sd-face-seltype*
*sd-edge-3d-seltype*
*sd-vertex-3d-seltype*)
:incl-position :3d
:after-input
(progn
(when POLESTAR
(sd-delete-polestar POLESTAR))
(setq POLESTAR
(sd-create-polestar
:pick-token ":DRAG_VARIABLE"
:components (sd-classic-polestar-components
(first FEV) (second FEV)))))
)
(DRAG_VARIABLE
:drag-from-polestar POLESTAR
:polestar-passenger t
:quickview-type :qv-parcel
:quickview-parcels (list (first FEV))
)
)
)
Note that the repositioning of the part is included with the quickview
functionality. Thus, no further :after-input code is required
to transfer the state of the dragged quickview to the model.
This example illustrates a dynamically created polestar, a dragger and a lisp-based quickview feedback.
The dialog allows the user to select a vertex of a wire part and to drag that vertex along the neighboring edges, or within the plane spanned by those edges or perpendicular to that plane.
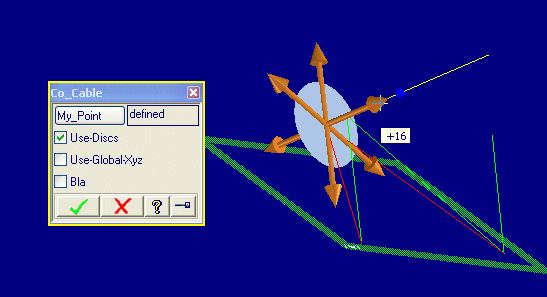
(sd-defdialog 'co_cable
:prompt-variable 'MY_POINT
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
:variables
`(
(POLESTAR :initial-value nil)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(NEIGHBORING-EDGES :initial-value nil)
(NEIGHBORING-PNTS :initial-value nil)
(DISC-DIRS :intiial-value nil)
(LINE-DIRS :intiial-value nil)
(FEEDBACKS :initial-value nil)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(MY_POINT
:selection *sd-vertex-3d-seltype*
:multiple-items nil
:wire-part-allowed t
:incl-position :3d
:after-input (make-polestar)
)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(USE-DISCS
:value-type :boolean
:after-input (make-polestar)
)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(USE-GLOBAL-XYZ
:value-type :boolean
:toggle-type :wide-toggle
:after-input (make-polestar)
)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(BLA
:value-type :boolean
)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(POLESTAR_PICK
:drag-from-polestar POLESTAR
:polestar-passenger t
:quickview-type :lisp-feedback
:feedback-update-function update-feedback
:feedback-destroy-function destroy-feedback
:feedback-apply-function apply-quickview
:end-input-feedback
(when (and POLESTAR (not POLESTAR_PICK)) ; dragging cancelled
(sd-delete-polestar POLESTAR)
(setq POLESTAR nil))
)
)
:local-functions
'(
;;==========================================================================
(make-polestar ()
(sd-delete-polestar POLESTAR)
(setq POLESTAR
(sd-create-polestar
:origin (second MY_POINT)
:pick-token ":POLESTAR_PICK"
:components (get-polestar-components))))
;;==========================================================================
(get-polestar-components ()
(set-qp-data (first MY_POINT))
(let ((components nil))
(dolist (dir LINE-DIRS)
(push (list :type :line :dir dir :origin (second MY_POINT)) components))
(dolist (dir DISC-DIRS)
(push (list :type :disc :dir dir :origin (second MY_POINT)) components))
components)
)
;;==========================================================================
(set-qp-data (vertex)
(setq NEIGHBORING-EDGES
(sd-call-cmds (GET_SELECTION :select :edge_3d :by_vertex_3d vertex)))
(setq NEIGHBORING-PNTS nil)
(dolist (edge NEIGHBORING-EDGES)
(let* ((struc (sd-inq-edge-geo edge :dest-space :global))
(pnt (cond ((equal (sd-edge-start-pnt struc)
(second MY_POINT))
(sd-edge-end-pnt struc))
((equal (sd-edge-end-pnt struc)
(second MY_POINT))
(sd-edge-start-pnt struc)))))
(when pnt
(push pnt NEIGHBORING-PNTS))))
(setq LINE-DIRS nil)
(setq DISC-DIRS nil)
;; Build a list of non parallel vectors
(dolist (edge NEIGHBORING-EDGES)
;; only works for lines as we don't know whether it's the start or
;; end of the edge that is incident at our vertex. For lines this
;; does not matter.
(let ((sd-curve (sd-inq-geo-props edge :dest-space :global)))
(when (sd-line-p sd-curve)
(let ((dir (sd-line-dir sd-curve)))
(when (not (vec-parallel-to-any dir LINE-DIRS))
(setq LINE-DIRS (cons dir LINE-DIRS)))
)
)
)
)
(when USE-GLOBAL-XYZ
;; Use global x,y,z rather than the neighbouring edge basis.
(setq LINE-DIRS '(1,0,0 0,1,0 0,0,1))
(when USE-DISCS (setq DISC-DIRS LINE-DIRS))
)
;; We expect 1 or 2 dirs
(case (length LINE-DIRS)
(1 ;; Add two ortho normal lines
(setq LINE-DIRS (cons (vec-orthogonal (first LINE-DIRS)) LINE-DIRS))
(setq LINE-DIRS (cons (sd-vec-normalize (sd-vec-cross-product
(first LINE-DIRS)
(second LINE-DIRS)))
LINE-DIRS)
)
;; And make 2 planes !
(when USE-DISCS
(setq DISC-DIRS (cons (first LINE-DIRS) DISC-DIRS))
(setq DISC-DIRS (cons (second LINE-DIRS) DISC-DIRS))
)
)
(2 ;; Cross these two
(let ((dir (sd-vec-normalize (sd-vec-cross-product (first LINE-DIRS)
(second LINE-DIRS)))))
(unless (sd-vec-null-p dir)
(when USE-DISCS
(setq DISC-DIRS (cons dir DISC-DIRS))
)
(setq LINE-DIRS (cons dir LINE-DIRS))
)
)
)
)
)
;;==========================================================================
(update-feedback (quickview)
; 1. delete existing feedbacks
(destroy-feedback quickview)
; 2. create new feedbacks
(let ((pos (get-quickview-position quickview)))
(setf FEEDBACKS
(mapcar #'(lambda (start)
(sd-start-polyline-feedback
(list start pos) :color 1,0,0)
)
NEIGHBORING-PNTS)))
)
;;==========================================================================
(destroy-feedback (quickview)
(declare (ignore quickview))
(dolist (fb FEEDBACKS)
(sd-end-feedback fb))
(setf FEEDBACKS nil)
)
;;==========================================================================
(get-quickview-position (quickview)
(let* ((qv-result (sd-inq-quickview quickview :vector-transform))
(dir (getf qv-result :translation)))
(when dir
(sd-vec-add (second MY_POINT) dir))))
;;==========================================================================
(apply-quickview (qv)
(let ((pos (get-quickview-position qv)) ;; Get the new position
(part_sel ;; Find the part to modify, from the vertex
(sd-call-cmds
(get_selection :focus_type *sd-part-seltype*
:single_selection
:allow_wire_part
:select (second MY_POINT)))
)
)
(sd-delete-quickview 'POLESTAR_PICK)
;; delete the neighbouring edges and make new ones to the new pos
(sd-call-cmds
(progn
(dolist (edge NEIGHBORING-EDGES)
(curve_deletion edge)
)
(dolist (start-point NEIGHBORING-PNTS)
(create_straight :wire_part part_sel :two_points start-point pos)
)
)
)
;; Update MY_POINT and the polestar
(let ((vertex_sel
(sd-call-cmds
(get_selection :focus_type *sd-vertex-3d-seltype*
:single_selection
:select pos)
)
)
)
;; using set-variable-status forces the after-input to be run, which
;; remakes the polestar
(sd-set-variable-status 'MY_POINT :value (list vertex_sel pos))
)
)
)
)
)
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;; ;;
;; Vec Utils ;;
;; ;;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
(defun vec-parallel-to-any (vec vec-list)
(dolist (v vec-list)
(when (vec-parallel v vec)
(return-from vec-parallel-to-any t))
)
nil
)
;; There's no sd-vec-parallel that includes anti-parallel
(defun vec-parallel (vec1 vec2)
(let ((uvec1 (sd-vec-normalize vec1))
(uvec2 (sd-vec-normalize vec2)))
(or (equalp uvec1 uvec2)
(equalp uvec1 (sd-vec-scale uvec2 -1.0))))
)
(defun vec-orthogonal (vec)
(let ((x (gpnt3d_x vec))
(y (gpnt3d_y vec))
(z (gpnt3d_z vec))
(new-x)
(new-y)
(new-z))
;scalar product must be zero.
(if (or (> (* x x) 0) (> (* y y) 0))
(setq new-x (- y) new-y (- x) new-z 0)
(setq new-x (- z) new-y 0 new-z (- x)))
(sd-vec-normalize
(make-gpnt3d :x new-x :y new-y :z new-z)))
)
![Integration Kit What's New [Integration Kit What's New]](../Nav02_WhatsNew.png) |
| © 2025 Parametric
Technology GmbH (a subsidiary of PTC Inc.), All Rights Reserved |