Heat Models
Viscous Work
Viscous work allows you to include the contribution viscous forces to the energy equations. If you set Include Viscous Work to No, the fluid is treated as inviscid with regard to the energy equation.
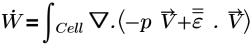
where,
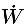 | work per second (J/s) |
p | pressure (Pa) |
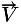 | surface normal |
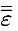 | viscous contribution to the stress tensor τij such that 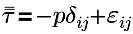 |
τij | stress tensor, force per unit area in the jth direction on a surface element with an outward unit normal in the ith direction |
Convection
Convection is a thermal boundary condition in which the heat flux is a function of convective heat transfer. This is also known as Newton Cooling. It is based on the external convection ambient temperature and an exchange coefficient (h) as shown below:
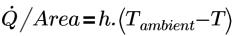
where,
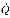 | Watts (J/s) |
h | exchange coefficient (W/m2-K) |
Tambient | convection ambient temperature (K) |
T | boundary temperature (K) |
Radiation
Radiation is a thermal boundary condition in which the heat flux is a function of radiative heat transfer, based on emissivity, and an external radiation ambient temperature.
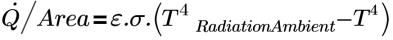
where,
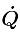 | Watts (J/s) |
ε | emissivity |
σ | Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.670 x10−8 (W/m2K4) |
TRadiation Ambient | radiation ambient temperature (K) |
T | boundary temperature (K) |