Definitions
• Component—An element or compound with its own chemical composition which mixes with the other components and has no distinct interface in between. Examples are salt in water, and gases nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide in air.
• Average Concentration—The concentration of the multicomponent integrated over a volume or area, based on a volume or area weighted average.
• Concentration—Mass fraction of the component relative to the fluid mass.
• Mass Avg. Concentration—Average concentration of the component integrated over a volume, based on a mass weighted average.
• Vol. Avg. Concentration—Average concentration of the component integrated over a volume, based on a volume weighted average.
• Species Mass—Total mass, measured in kg, of a component in a mixture volume.
• Diffusivity—A transport property that relates the flux of a component to the concentration gradient of the component 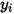 according to Fick’s law:
according to Fick’s law:
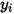 according to Fick’s law:
according to Fick’s law: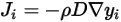
where,
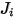 | multicomponent flux kg/m2-s |
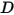 | diffusivity m2/s |
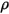 | fluid density kg/m3 |
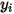 | concentration (mass fraction) of component  |
• Schmidt Number—Ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to species (mass) diffusivity.
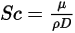
where 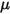 is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa-s).
is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa-s).
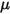 is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa-s).
is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa-s).• Flux per Area—Average flux (kg/m2) of a component crossing a selected boundary or interface.
• Total Flux—Total amount of a component in kg that crosses a selected boundary or interface.
• Volumetric Flux m3/s—Volumetric flux of a component crossing a selected boundary or interface.