About Legacy Flat State Instances
A flat state is a completely unbent copy of your part. It streamlines the creation of flat patterns needed in manufacturing because you can create any number of flat states, at any time in your design process, whether your part is fully formed or fully flat. Flat states are managed with family tables.
|
|
• The Flat State Instances property is available in the Model Properties dialog box of the generic model. You must have the enable_flat_state configuration option set to yes or a legacy flat state instance must be in the model.
• Best practice is to automatically create a flat pattern instance using the Create Instance button on Graphics toolbar of the Flat Pattern Preview window.
• You can also use standard family table commands to create flat state instances of a part with an Unbend or Flat Pattern feature.
|
With the flat state commands you can:
• Produce a new flat state instance with the Create command.
• Transfer any features you added specifically to a flat state from the flat state to the generic part with the Update command. The only exceptions are features you specifically suppressed. You can then delete or suppress desired features which, in turn, are deleted or suppressed in any other flat state in that part's family table.
• List the flat state instances related to the generic part you have open with the Show command. Select a flat state instance and it opens in a separate window. You can make any needed design changes.
|
Fully Formed Part
|
Flat State (original)
|
Flat State (modified)
|
|---|---|---|
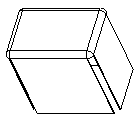 |
 |
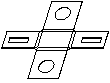 |
While flat states are copies of the generic part, you can edit individual flat state instances to make any necessary modifications. Any new features you add to a flat state are enabled in that specific flat state instance but suppressed in the generic part. Any features you delete from a flat state are suppressed in the specific flat state instance but still enabled in the generic part. Keep in mind that any features you add to the generic part, after you create the flat state, are added to all flat state instances.
When you create a flat state instance, the unbend or the flat state is automatically added to the end of the generic part's Model Tree. Any modifications made to the generic do not affect the flat state. Therefore, in the generic, a flat state works exactly as a flat pattern. Any features added to the generic are automatically reordered to always be inserted before the unbend.
When you create a flat state instance it automatically adds to the generic part's family table. And every feature change you make in the flat state instance records in the generic part's family table. A new feature receives a new column. A deleted feature also receives a new column, unless the appropriate column already exists.
|
|
Features added to flat state instances behave like features added to regular family table parts. However, if you suppress a flat protrusion or unbend, you cannot resume them with the Resume All command. You must resume those features individually ( > or > ).
|