Keys and Key References Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to view information about the key definitions and key references in a DITA map and the topics and maps that map references. If the key context for the current map is set to another DITA map, the information in the dialog box is for the map that is the key context, not the current map. You can also open this dialog box from a DITA topic, but in this case it only contains information about the key references contained in that topic and the associated definitions for those references as defined in the map that is the current key context. If it takes more than a few seconds for the dialog box to gather and display the key information, a progress bar is displayed.
Note that for a key reference to have information about its key definition, it must have an active key context and the associated key must be defined in that context. A key context is a DITA map containing key definitions. The value assigned to the ditakeycontext set option determines the key context for a document. This option can be set explicitly or Arbortext Editor sets it automatically for certain cases. For example, if you open a referenced topic from a map that contains key definitions, that map becomes the key context.
You invoke this dialog box from the > menu choice. You can also use the Find Key References menu choice on both the Tools menu and shortcut menu to open this dialog box in a DITA map for just the keys defined in the tag containing the cursor.
The Keys and Key References dialog box contains the following options:
• Key and key reference information — Provides information about the key definitions and associated key references in the current document.
This area of the dialog box lists both the key definition defined in the map and where those keys are used in the documents referenced from the map. It also shows any other key references defined in the documents referenced from the current map that do not have an associated key definition in the current key context. For keys with definitions and key references, you can click on the definition or reference in the tree to select it and then use the Go To button to open the document containing that key definition or reference.
For keys with definitions, a key icon appears
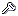
followed by the name of the key and the value of the
href attribute in the definition. If there are references to this key in the map or in documents referenced from the map, those references are nested below the key definition. You can collapse and expand the list of references below the key. The element containing the listed key reference is indicated by the following icons:
◦ 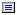
— Indicates a topic reference (
topicref).
For this and the other key references (in the keyref attribute), the icon is followed by the name of the element containing the key reference followed by the file name of the document containing the reference. If the document containing the reference is in a content management system (CMS) instead of on the file system, the name is either the CMS object name or the Logical ID.
◦ 
— Indicates a cross reference (
xref) or
link.
◦ 
— Indicates an
image.
◦ 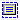
— Indicates a content key reference .
For content key references, (in the conkeyref attribute), the icon is followed by the name of the element in the document that is the target of the content reference followed by the file name of the document containing the reference followed by (conkeyref).
For key references that do not have an associated definition, a key icon with a red x appears

followed by the name of the key in the key reference followed by
(no definition). Below this are the references to the undefined key that have been located in the documents referenced from the current map.
• Expand All — Expands all of the key references beneath the listed keys.
• Collapse All — Collapses all of the key references beneath the listed keys.
• Go To — Opens the document containing the selected key definition or reference and highlights that key definition in the document.
• Refresh — Updates the list of key definitions to their latest state.
Related information
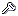 followed by the name of the key and the value of the href attribute in the definition. If there are references to this key in the map or in documents referenced from the map, those references are nested below the key definition. You can collapse and expand the list of references below the key. The element containing the listed key reference is indicated by the following icons:
followed by the name of the key and the value of the href attribute in the definition. If there are references to this key in the map or in documents referenced from the map, those references are nested below the key definition. You can collapse and expand the list of references below the key. The element containing the listed key reference is indicated by the following icons: followed by the name of the key and the value of the href attribute in the definition. If there are references to this key in the map or in documents referenced from the map, those references are nested below the key definition. You can collapse and expand the list of references below the key. The element containing the listed key reference is indicated by the following icons:
followed by the name of the key and the value of the href attribute in the definition. If there are references to this key in the map or in documents referenced from the map, those references are nested below the key definition. You can collapse and expand the list of references below the key. The element containing the listed key reference is indicated by the following icons: — Indicates a topic reference (
— Indicates a topic reference ( — Indicates a cross reference (
— Indicates a cross reference ( — Indicates an
— Indicates an  — Indicates a content key reference .
— Indicates a content key reference . followed by the name of the key in the key reference followed by
followed by the name of the key in the key reference followed by