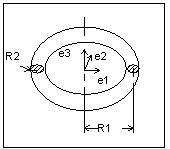
Example: Torus Data Format
The generating curve of a torus is an arc of radius R2 with its center at a distance R1 from the origin. R1 cannot equal zero. The starting point of the generating arc is located at a distance R1 + R2 from the origin, in the direction of the first vector of the local coordinate system. The radial distance of a point on the torus is R1 + R2 * cos(v), and the height of the point along the axis of revolution is R2 * sin(v). The following illustration shows a torus.
Data format:
e1[3] | (dbl) | |
e2[3] | (dbl) | |
e3[3] | (dbl) | |
origin[3] | (dbl) | Origin of the local coordinate system |
R1 | (dbl) | The distance from the center of the generating arc to the axis of revolution |
R2 | (dbl) | The radius of the generating arc |
Parameterization:
(x, y, z) = (R1 + R2 * cos(v)) * [cos(u) * e1 + sin(u) * e2] + R2 * sin(v) * e3 + origin