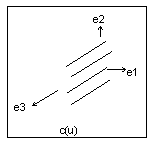
Example: Tabulated Cylinder Data Format
The system calculates a tabulated cylinder by projecting a curve linearly through space. It evaluates the curve at the u parameter, and offsets the z-coordinate by the v parameter. It expresses the resulting point in local coordinates and must transform it by the local coordinate system to express it in part coordinates. The following illustration shows a tabulated cylinder.
Data format:
e1[3] | (dbl) | |
e2[3] | (dbl) | |
e3[3] | (dbl) | |
origin[3] | (dbl) | Origin of the local coordinate system |
C | (curve structure) | Generating curve |
Parameterization:
(x', y', z')is the point in local coordinates
(x', y', z') = C(u) + (0, 0, v)
(x, y, z) = x' * e1 + y' * e2 + z' * e3 + origin