To Modify a Curve or a One-Sided Edge
1. Select a 3D, UV-curve, or one-sided edge that you want to modify. You can select a curve either in the graphics window or on the GTS Tree. You can select one-sided edges in the graphics window.
|
|
• A one-sided edge is converted to a UV-spline when you modify it. After modification, the UV-spline is converted back to a one-sided edge. If the resulting geometry overlaps, the modify process is aborted and the geometry is not affected.
• If the modified one-sided edge belongs to a component, on exiting the Modify tool, if possible, two-sided edge gets automatically created with the adjacent surface in same component.
|
2. Click
Edit >
 Modify
Modify on the
Import DataDoctor tab or right-click the selected curve or one-sided edge and click
Modify. The
Modify Curve dialog box opens.
3. Perform one of the following curve modification operations:
◦ Click
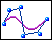
to modify the curve using its control points and select a point on the curve to move.
◦ Click
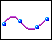
to modify the curve using its interpolation points and click one of the following options for interpolation points in the
Modify Curve dialog box:
▪ Move—Moves the selected interpolation point on the curve.
▪ Add—Adds an interpolation point to the curve at the selected location.
▪ Delete—Deletes the selected interpolation point from the curve.
▪ Redistribute—Redistributes the interpolation points on the curve according to the curvature of the curve.
4. To specify the movement options for the curve, select one of the following options under Movement options:
◦ Curve plane—Restricts curve movement to the curve plane only. A curve plane is a plane formed by the tangent and the normal vector of the curve.
◦ 3D movement—Moves the curve freely in 3D space.
◦ Local—Moves only the selected control point.
◦ Smooth region—Moves the control points by a distance relative to the selected point. The point movement distance decreases in proportion to its distance from the selected point by a cubic rule.
◦ Linear region—Moves the control points by a distance relative to the selected point. The point movement distance decreases in proportion to its distance from the selected point by a linear rule.
◦ Constant region—Moves all the control points by the same distance from the selected point. For a constrained surface, the boundary does not move.
5. Select and drag a vertex on the curve to modify the curve. Alternatively, specify increment values for the following Fine control options for finer control of point movement:
◦ Normal direction—Specifies the increment in the normal direction.
◦ Tangent direction—Specifies the increment in the tangent direction.
◦ Bi-normal direction—Specifies the increment in the binormal direction.
◦ Increment—Specifies the value of the point movement increment.
6. Click Apply to apply the changes made to the curve.
7. Click OK to quit the Modify Curve dialog box.
 Modify on the Import DataDoctor tab or right-click the selected curve or one-sided edge and click Modify. The Modify Curve dialog box opens.
Modify on the Import DataDoctor tab or right-click the selected curve or one-sided edge and click Modify. The Modify Curve dialog box opens. Modify on the Import DataDoctor tab or right-click the selected curve or one-sided edge and click Modify. The Modify Curve dialog box opens.
Modify on the Import DataDoctor tab or right-click the selected curve or one-sided edge and click Modify. The Modify Curve dialog box opens. to modify the curve using its control points and select a point on the curve to move.
to modify the curve using its control points and select a point on the curve to move. to modify the curve using its interpolation points and click one of the following options for interpolation points in the
to modify the curve using its interpolation points and click one of the following options for interpolation points in the